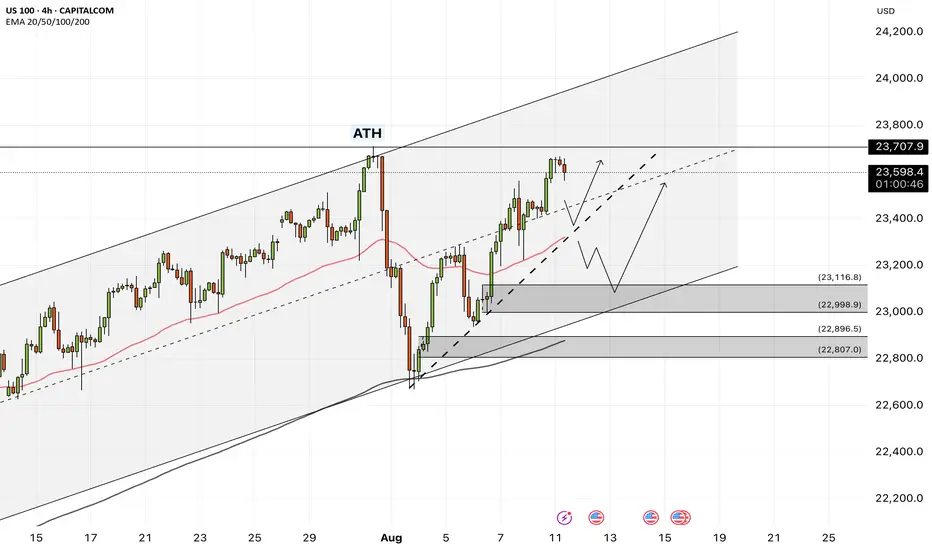
The index is above the EMA200 and EMA50 on the four-hour timeframe and is trading in its ascending channel. If the index corrects downwards towards the drawn trend line or the specified demand zone, you can buy Nasdaq with better reward for risk.
Many Federal Reserve officials believe that tariffs could weaken the U.S. economy and push inflation higher—a dilemma that forces policymakers to choose between cutting interest rates to support growth or keeping them unchanged to control prices.
However, Miran—the economic adviser President Donald Trump intends to nominate to the Fed’s Board of Governors—rejects this view. He argues that tariffs will ultimately benefit the economy and will not significantly impact prices, allowing the Fed to resume the rate-cutting cycle it halted earlier this year.
The key question now is whether Miran’s arguments will be persuasive enough to sway the broader thinking of the central bank’s policy committee, or whether concerns over labor market weakness might prompt rate cuts regardless, rendering his arguments unnecessary.
According to analysis from The Wall Street Journal, beyond the policy disagreements, Miran has also challenged the institutional legitimacy of the Federal Reserve. He has accused Fed officials of having political motivations and criticized them for what he calls the “tariff disruption syndrome.” In a paper published last year, he argued that all senior Fed officials should be subject to dismissal at the White House’s discretion. If appointed, he would give Trump a loyal ally inside the Fed’s boardroom—someone capable of promoting the president’s views and challenging the institution’s consensus-driven culture and influential research staff.
Meanwhile, JPMorgan has revised its monetary policy forecast for 2025, now expecting the Fed to deliver three 25-basis-point rate cuts starting in September 2025, compared to its earlier projection of just one cut in December.
Miran, who holds a Ph.D. in economics from Harvard University, currently serves as Chairman of the White House Council of Economic Advisers. On Thursday, Trump announced his intention to nominate him for a newly vacant Fed board seat. This position became available unexpectedly after Adriana Kugler’s resignation last week and will expire in January. Trump also revealed plans to nominate another individual to fill this seat, who could potentially replace Jerome Powell as Fed Chair in the spring. Miran’s appointment would give Trump additional time to evaluate how candidates—whether Miran himself or Christopher Waller, whom he appointed during his first term—align with his policy views and vote on interest rates.
This week’s economic calendar is once again crowded, with a series of key inflation reports and consumer-related indicators in the spotlight.
Early Tuesday, the Reserve Bank of Australia will announce its interest rate decision, with markets expecting a 25-basis-point cut from 3.85% to 3.60%. Shortly after, traders’ attention will shift to the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) for July, where core inflation is expected to rise from 0.2% in June to 0.3%.
Wednesday will be relatively quiet, with the main highlight being speeches from Fed officials Austan Goolsbee and Raphael Bostic. On Thursday, focus will return to major data releases, including the U.S. Producer Price Index (PPI), which is projected to see its core measure increase by 0.2% after holding steady in June. Weekly jobless claims figures will also be released that day.
The week will conclude with a broader look at U.S. consumer activity. July retail sales are forecast to slow from 0.6% to 0.5%, while core retail sales are expected to drop from 0.6% to 0.3%. Hours later, the preliminary August reading of the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index will be released, providing insights into consumer expectations and confidence.
According to ISM data, pricing pressures have eased in the manufacturing sector but have jumped sharply in the services sector, which makes up a much larger share of the U.S. economy. This suggests that upcoming CPI and PPI reports carry an upside risk relative to forecasts. Inflation readings above expectations—even before fully factoring in the impact of retaliatory tariffs—could erase part of the market’s anticipated rate-cut outlook.
Many Federal Reserve officials believe that tariffs could weaken the U.S. economy and push inflation higher—a dilemma that forces policymakers to choose between cutting interest rates to support growth or keeping them unchanged to control prices.
However, Miran—the economic adviser President Donald Trump intends to nominate to the Fed’s Board of Governors—rejects this view. He argues that tariffs will ultimately benefit the economy and will not significantly impact prices, allowing the Fed to resume the rate-cutting cycle it halted earlier this year.
The key question now is whether Miran’s arguments will be persuasive enough to sway the broader thinking of the central bank’s policy committee, or whether concerns over labor market weakness might prompt rate cuts regardless, rendering his arguments unnecessary.
According to analysis from The Wall Street Journal, beyond the policy disagreements, Miran has also challenged the institutional legitimacy of the Federal Reserve. He has accused Fed officials of having political motivations and criticized them for what he calls the “tariff disruption syndrome.” In a paper published last year, he argued that all senior Fed officials should be subject to dismissal at the White House’s discretion. If appointed, he would give Trump a loyal ally inside the Fed’s boardroom—someone capable of promoting the president’s views and challenging the institution’s consensus-driven culture and influential research staff.
Meanwhile, JPMorgan has revised its monetary policy forecast for 2025, now expecting the Fed to deliver three 25-basis-point rate cuts starting in September 2025, compared to its earlier projection of just one cut in December.
Miran, who holds a Ph.D. in economics from Harvard University, currently serves as Chairman of the White House Council of Economic Advisers. On Thursday, Trump announced his intention to nominate him for a newly vacant Fed board seat. This position became available unexpectedly after Adriana Kugler’s resignation last week and will expire in January. Trump also revealed plans to nominate another individual to fill this seat, who could potentially replace Jerome Powell as Fed Chair in the spring. Miran’s appointment would give Trump additional time to evaluate how candidates—whether Miran himself or Christopher Waller, whom he appointed during his first term—align with his policy views and vote on interest rates.
This week’s economic calendar is once again crowded, with a series of key inflation reports and consumer-related indicators in the spotlight.
Early Tuesday, the Reserve Bank of Australia will announce its interest rate decision, with markets expecting a 25-basis-point cut from 3.85% to 3.60%. Shortly after, traders’ attention will shift to the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) for July, where core inflation is expected to rise from 0.2% in June to 0.3%.
Wednesday will be relatively quiet, with the main highlight being speeches from Fed officials Austan Goolsbee and Raphael Bostic. On Thursday, focus will return to major data releases, including the U.S. Producer Price Index (PPI), which is projected to see its core measure increase by 0.2% after holding steady in June. Weekly jobless claims figures will also be released that day.
The week will conclude with a broader look at U.S. consumer activity. July retail sales are forecast to slow from 0.6% to 0.5%, while core retail sales are expected to drop from 0.6% to 0.3%. Hours later, the preliminary August reading of the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index will be released, providing insights into consumer expectations and confidence.
According to ISM data, pricing pressures have eased in the manufacturing sector but have jumped sharply in the services sector, which makes up a much larger share of the U.S. economy. This suggests that upcoming CPI and PPI reports carry an upside risk relative to forecasts. Inflation readings above expectations—even before fully factoring in the impact of retaliatory tariffs—could erase part of the market’s anticipated rate-cut outlook.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.