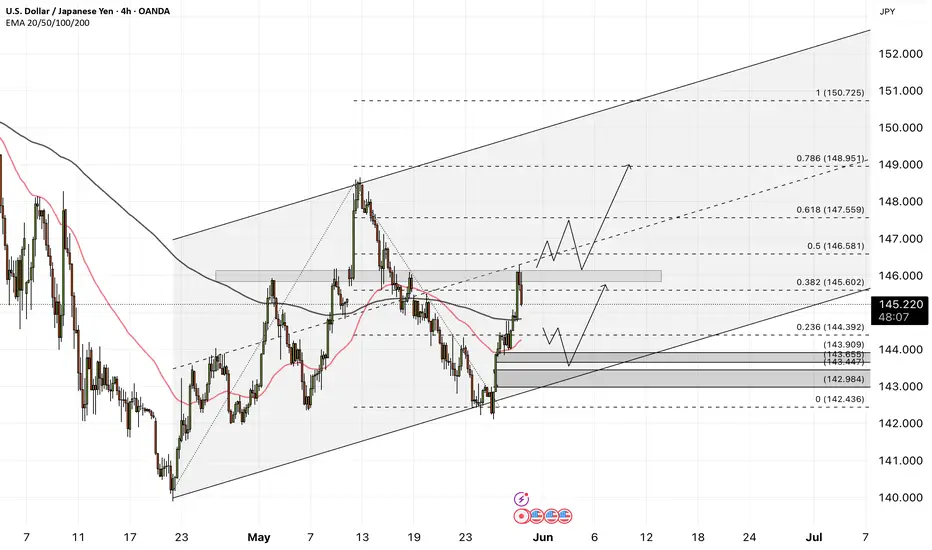
The USDJPY currency pair is above the EMA200 and EMA50 on the 4-hour timeframe and is moving in its ascending channel. In case of correction due to the release of today's economic data, we can see a downward trend and then see the demand zone and buy in that range with an appropriate risk-reward ratio. A credible break of the indicated resistance range will pave the way for the currency pair to rise.
Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba emphasized that investment is more crucial to economic growth than tariffs, reaffirming Japan’s continued commitment to negotiating the removal of U.S. trade tariffs. He also pointed to encouraging signs in the Japanese economy following wage increases and offered an optimistic outlook on the country’s recovery.
Meanwhile, Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda, speaking on Wednesday, warned that significant volatility in ultra-long-term bond yields could affect short-term borrowing costs, which in turn might exert a stronger impact on the broader economy. His remarks highlight the BOJ’s growing focus on recent fluctuations in long-dated bond yields, which could influence the board’s decision next month regarding the pace of its bond purchase reduction.
Ueda explained that in Japan, short- and medium-term interest rates tend to have more direct influence on the economy than ultra-long yields, due to the maturity structure of household and corporate debt. However, he acknowledged in a parliamentary session that sharp moves in ultra-long yields can also affect long- and even short-term bond yields indirectly.
Turning to Friday’s inflation report, expectations suggest that overall inflation remained subdued in April, as falling gasoline prices provided some relief to household budgets. However, core inflation—excluding food and energy—remains stubbornly high.
The PCE inflation index is anticipated to have risen 2.2% in April from a year earlier, slightly down from 2.3% in March, marking the lowest level since last September. Federal Reserve officials are still awaiting more data on how newly imposed tariffs are feeding into the broader economy, making it unlikely that the recent moderation in inflation will prompt a rate cut in the near term.
Although the Fed’s preferred inflation measure may have reached its lowest point since September, a second consecutive month of encouraging price data is unlikely to be sufficient to justify easing interest rates.
According to a survey conducted by Dow Jones Newswires and The Wall Street Journal, economists expect Friday’s report—covering inflation, income, and spending—from the Bureau of Economic Analysis to show that consumer prices rose 2.2% year-over-year through April. This would mark the lowest reading since September and a potential turning point in the Fed’s battle against post-pandemic inflation.
Goldman Sachs economists noted that falling gasoline prices have more than offset the inflationary impact of new tariffs introduced by the Trump administration. However, they cautioned that this dynamic may not last, as retailers are likely to start passing along the added import tax costs to consumers in the coming months.
Several Federal Reserve officials, concerned that tariffs could reignite inflation, have stated that they will wait to assess the full impact of these trade policies on the economy before making changes to the federal funds rate—which directly affects borrowing costs on everything from mortgages and auto loans to credit cards.
Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba emphasized that investment is more crucial to economic growth than tariffs, reaffirming Japan’s continued commitment to negotiating the removal of U.S. trade tariffs. He also pointed to encouraging signs in the Japanese economy following wage increases and offered an optimistic outlook on the country’s recovery.
Meanwhile, Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda, speaking on Wednesday, warned that significant volatility in ultra-long-term bond yields could affect short-term borrowing costs, which in turn might exert a stronger impact on the broader economy. His remarks highlight the BOJ’s growing focus on recent fluctuations in long-dated bond yields, which could influence the board’s decision next month regarding the pace of its bond purchase reduction.
Ueda explained that in Japan, short- and medium-term interest rates tend to have more direct influence on the economy than ultra-long yields, due to the maturity structure of household and corporate debt. However, he acknowledged in a parliamentary session that sharp moves in ultra-long yields can also affect long- and even short-term bond yields indirectly.
Turning to Friday’s inflation report, expectations suggest that overall inflation remained subdued in April, as falling gasoline prices provided some relief to household budgets. However, core inflation—excluding food and energy—remains stubbornly high.
The PCE inflation index is anticipated to have risen 2.2% in April from a year earlier, slightly down from 2.3% in March, marking the lowest level since last September. Federal Reserve officials are still awaiting more data on how newly imposed tariffs are feeding into the broader economy, making it unlikely that the recent moderation in inflation will prompt a rate cut in the near term.
Although the Fed’s preferred inflation measure may have reached its lowest point since September, a second consecutive month of encouraging price data is unlikely to be sufficient to justify easing interest rates.
According to a survey conducted by Dow Jones Newswires and The Wall Street Journal, economists expect Friday’s report—covering inflation, income, and spending—from the Bureau of Economic Analysis to show that consumer prices rose 2.2% year-over-year through April. This would mark the lowest reading since September and a potential turning point in the Fed’s battle against post-pandemic inflation.
Goldman Sachs economists noted that falling gasoline prices have more than offset the inflationary impact of new tariffs introduced by the Trump administration. However, they cautioned that this dynamic may not last, as retailers are likely to start passing along the added import tax costs to consumers in the coming months.
Several Federal Reserve officials, concerned that tariffs could reignite inflation, have stated that they will wait to assess the full impact of these trade policies on the economy before making changes to the federal funds rate—which directly affects borrowing costs on everything from mortgages and auto loans to credit cards.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.