OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Updated Bitcoin Price to Volume per $1 Fee
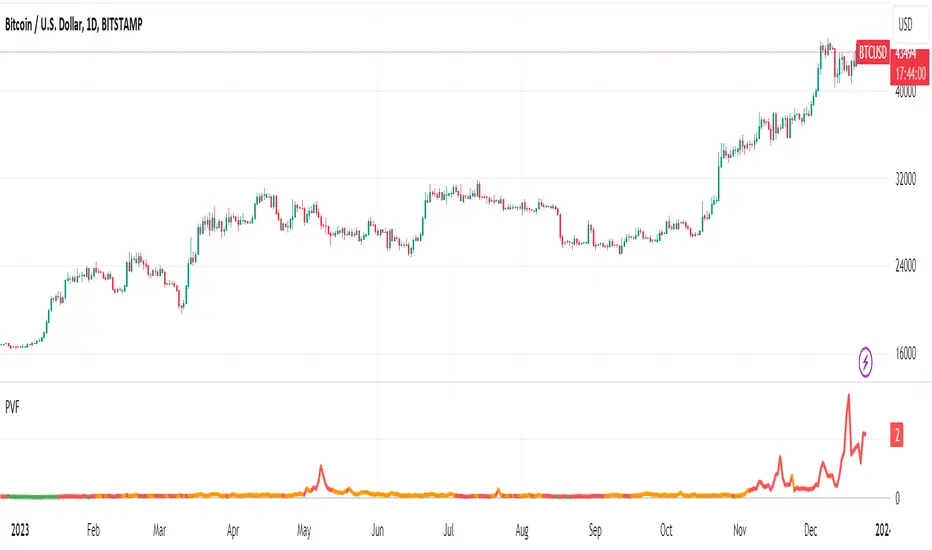
Transaction value to transaction fee:
The Bitcoin network's efficiency, usability and volume scalability has been improving over time and this can be measured by dividing the average transaction volume by the transaction fee.
The indicator give us:
Price to volume per $1 fee = BTC price / (avg tx value / avg tx fee)
A low ratio of "Price to volume per $1 fee" indicates that the Bitcoin network is being used for high volumes in comparison to the Bitcoin price, which means that the network is cost-effective compared to the price. On the other hand, a high "Price to volume per $1 fee" suggests that the average transaction size is smaller than the price of Bitcoin, which means that the network is less cost-effective compared to the Bitcoin price.
Note that the dynamics of transaction fees may change over time as new use cases emerge in the Bitcoin chain. These use cases include L2s such as Stacks, where DeFi applications can run, and Bitcoin Ordinals.
It's worth mentioning that Bitcoin is not only a cost-effective way of transferring value, but also highly energy efficient. Despite receiving criticism for its energy consumption, when we compare its energy usage to other industries (such as banking and gold) and correlate it with the transaction volumes, we can easily conclude that Bitcoin's energy efficiency is remarkable when compared to other methods of transferring value.
The Bitcoin network's efficiency, usability and volume scalability has been improving over time and this can be measured by dividing the average transaction volume by the transaction fee.
The indicator give us:
Price to volume per $1 fee = BTC price / (avg tx value / avg tx fee)
A low ratio of "Price to volume per $1 fee" indicates that the Bitcoin network is being used for high volumes in comparison to the Bitcoin price, which means that the network is cost-effective compared to the price. On the other hand, a high "Price to volume per $1 fee" suggests that the average transaction size is smaller than the price of Bitcoin, which means that the network is less cost-effective compared to the Bitcoin price.
Note that the dynamics of transaction fees may change over time as new use cases emerge in the Bitcoin chain. These use cases include L2s such as Stacks, where DeFi applications can run, and Bitcoin Ordinals.
It's worth mentioning that Bitcoin is not only a cost-effective way of transferring value, but also highly energy efficient. Despite receiving criticism for its energy consumption, when we compare its energy usage to other industries (such as banking and gold) and correlate it with the transaction volumes, we can easily conclude that Bitcoin's energy efficiency is remarkable when compared to other methods of transferring value.
Release Notes
Updated from v4 to v5Open-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.
Open-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.