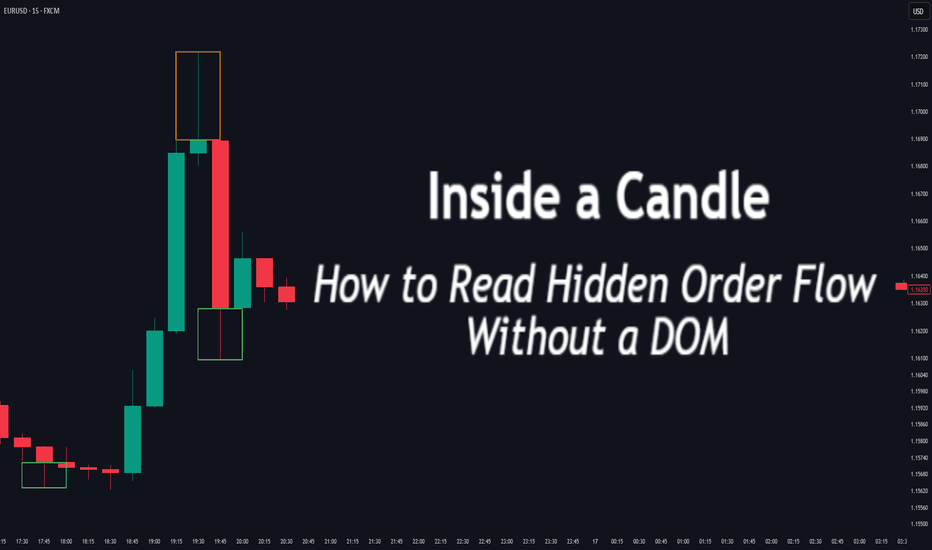
Inside a Candle: How to Read Hidden Order Flow Without a DOM
Difficulty: 🐳🐳🐳🐋🐋 (Intermediate+)
This article is for traders who want to understand the “story” behind a candle’s shape — and learn to spot aggressive buying/selling, absorption, and traps without needing footprint or order book tools.
🔵 INTRODUCTION
Most traders see candles as static shapes — green or red, big or small. But each candle is a battlefield of orders . Even without access to a DOM or volume footprint, you can still extract valuable information from just the candle's body, wick, and context .
🔵 ORIGINS: WHERE CANDLESTICKS COME FROM
Candlestick charts trace back to 18th-century Japan, where rice traders needed a way to visualize price movements over time. A legendary trader named Munehisa Homma , who traded rice futures in Osaka, is credited with developing the earliest form of candlestick analysis.
Homma discovered that price wasn’t just driven by supply and demand — but also by trader psychology . He created visual representations of market sentiment by tracking:
The opening and closing price of rice
The highest and lowest price reached during the session
This system became known as the “Sakata rules,” and it laid the foundation for many patterns still used today — such as Doji, Engulfing, and Marubozu.
Western traders only began using candlesticks widely in the 1990s, when analyst Steve Nison introduced them to the broader financial world through his book Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques.
Today, candlesticks remain one of the most powerful and intuitive ways to visualize order flow, momentum, and market psychology — even without a Depth of Market (DOM) or depth of book.
In this article, you’ll learn how to read hidden order flow by analyzing:
Wick length and positioning
Body-to-range ratios
Candle clustering and sequences
🔵 HOW A CANDLE FORMS
Before you can read a candle, you need to understand how it comes to life . A single candle represents the full auction process during its time window.
Here’s how it builds, step by step:
Candle opens — this is the open price .
As price moves up during the session → the high] updates.
As price moves down → the low] updates.
The final traded price when the time closes → this becomes the close price .
The wick = price areas that were tested but rejected
The body = where the majority of aggressive trades occurred
If buyers push price up quickly but sellers slam it down before the close — the candle will have a long upper wick and close near the open, revealing seller absorption.
Understanding this flow helps you recognize traps, fakeouts, and reversals in real time.
🔵 CANDLE BODY: WHO'S IN CONTROL
The body of the candle reflects the result of the battle between buyers and sellers. A wide body with minimal wicks means dominance and commitment.
Big body, small wick → clear conviction
In an uptrend: buyer aggression
In a downtrend: panic or aggressive selling
Small body, long wicks → indecision, absorption, or trap
Often appears near tops/bottoms
Indicates both sides were active but neither won clearly
tradingview.sweetlogin.com
🔵 WICKS: THE SHADOWS OF REJECTION
Wicks are not just “leftovers” — they show where price was rejected after being tested.
Long upper wick = seller presence or absorption at highs
Long lower wick = buyer defense or trap spring
Double wick = liquidity sweep / false breakout
Use wick direction to spot:
Failed breakouts
Smart money traps
Exhaustion candles
🔵 HIDDEN ORDER FLOW PATTERNS
1️⃣ Absorption Candle
A large wick with little movement afterward — shows that big orders absorbed market pressure.
2️⃣ Trap Candle
A candle that sweeps above/below a key high/low and closes opposite — classic smart money fakeout.
3️⃣ Imbalance Candle
Large-bodied candle that closes near the high/low with no wick on the other end — implies one-sided aggression (and often leaves an imbalance).
🔵 CLUSTERING & SEQUENCES MATTER
Never read a candle alone. The sequence of candles tells the full story:
3+ rejection wicks near resistance? Liquidity building before breakout or trap
Bearish engulfing after long upper wick = smart money selling into retail buying
Tight-range dojis + volume spike = compression before expansion
Context + volume + structure = hidden flow decoded.
🔵 PUTTING IT TOGETHER: A REAL EXAMPLE
Price breaks above previous high
Candle closes with long upper wick and smaller body
Next candle opens, dumps fast, leaving imbalance behind
Buyers trapped — move likely to continue down
This is how you read order flow from candle anatomy .
🔵 TIPS FOR MASTERY
Use a lower timeframe (1M–5M) to see microstructure
Watch how wicks behave near S/R or OBs
Confirm with volume spikes or delta-style indicators
Use replay mode to slow down the story and study cause/effect
🔵 CONCLUSION
Every candle is a message. You don’t need expensive tools to read order flow — just your eyes, context, and curiosity.
Learn to see candles not as symbols, but as evidence of behavior . Absorption, imbalance, and traps are all visible if you look closely.
Community ideas
Deep Dive Into Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)🗓 The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is one of the most popular momentum indicators in technical analysis. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding how the MACD works can significantly enhance your trading decisions.
📚 Introduction: What Is MACD and Why It Matters
The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is one of the most powerful and widely used momentum indicators in technical analysis. It was developed by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s and has since become a staple in the toolkit of traders and investors across markets — from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies.
At its core, MACD helps traders understand the relationship between two moving averages of an asset’s price, providing insight into both trend direction and momentum strength. By analyzing how these averages converge and diverge, the indicator offers valuable signals for entries, exits, and trend reversals.
What makes MACD especially popular is its versatility — it works well in trending markets, can be used across all timeframes, and combines both leading and lagging components. Whether you're a day trader or a long-term investor, understanding how MACD works gives you an edge in making timely and informed trading decisions.
📚 How the MACD Is Calculated: The Components Explained
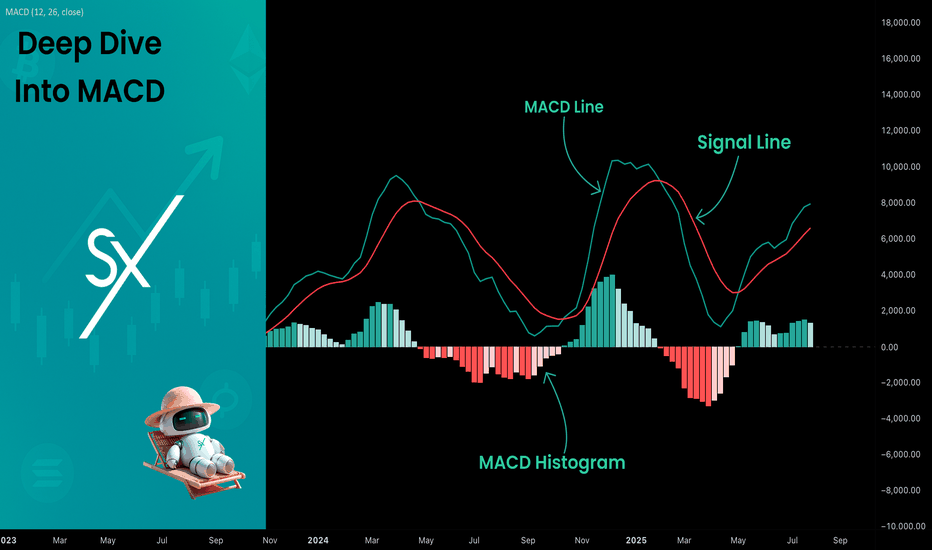
The MACD is built from three core components: MACD line, Signal line and MACD histogram.
🔹 Calculating the MACD Line:
The MACD line is the difference between two Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), typically 12-period EMA (fast) and 26-period EMA (slow). The formula is:
MACD Line = EMA(12) − EMA(26)
This line captures momentum by tracking how the shorter-term average diverges from the longer-term average. When the MACD line rises, the short-term momentum is increasing faster than the longer-term trend — a sign of bullish acceleration. The reverse implies bearish momentum.
🔹 Calculating the Signal Line:
To reduce noise and provide clearer signals, a 9-period EMA of the MACD line is plotted on top. This is the Signal Line, and it acts as a trigger:
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line → bullish signal (buy)
When the MACD line crosses below the signal line → bearish signal (sell)
Signal Line = EMA(9)(MACD Line)
🔹 Calculating the MACD Histogram:
The Histogram shows the difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line:
Histogram = MACD Line − Signal Line
It provides a visual representation of momentum strength. The histogram bars expand when momentum strengthens and contract as it fades. It helps you spot shifts in momentum earlier than a basic crossover.
📚 How to Use MACD in Trading Strategies
⚡️MACD Signal Line Crossover
Buy Signal:
MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line from below (bullish crossover)
Preferably when both lines are below the zero line (early in the trend)
Price closes above the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
Sell Signal:
MACD Line crosses below the Signal Line from above (bearish crossover)
Preferably when both lines are above the zero line (early in the trend)
Price closes below the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Wait until MACD line crosses over the Signal line from down to up. In our example we use 1D time frame for BITMART:BTCUSDT.P . Open long trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed above the 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Close the long trade when the MACD line crosses under the Signal line. This is an approximation that short-term impulse is over and correction is about to start.
In our case we have +20% return on this long trade, but, please, notice that we have not used initial stop-loss in this strategy. Trade was closed according to the technical condition, this approach can violate the risk management rules, but also can be applicable if you trade the amount ready to lose using this strategy. We will talk about stop-loss later.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Wait until MACD line crosses under the Signal line from up to down. In our example we use 1D time frame for BITMART:ETHUSDT . Open short trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed below the 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Close the short trade when the MACD line crosses over the Signal line. This is an approximation that short-term impulse is over and correction is about to start.
In this case we have +15% return on the short trade. Again, strategy used the technical condition to close the trade and now let's cover how to place the stop-loss. There is no right answer how to use stop-losses. The first and the most obvious way to place stop-loss is using recent swing low/high, but the problem is that all traders are seeing them and do the same. Price tends to reach such levels to collect liquidity.
Another one way to place stop-loss is using the signal candle's high/low. This is so-called 1 candle stop-loss. Usually it's very tight and can allow to have the fantastic risk to reward ratio, but we are now recommend to use it if you are not a professional trader because win rate of such strategy decreases.
Third approach in placing stop-loss which we often use in our algorithmic strategies is the Average True Range (ATR). ATR is the volatility measurement, it allows to take into account the current volatility. Sometimes it helps to avoid the stop-loss hit when trade finally goes in your direction. You can just simply subtract (in case of long trade) or add (in case of short trade) ATR value to the entry price and obtain the dynamic stop loss based on current market condition. Also multiplier can be used for ATR. You shall choose the approach which is more comfortable for you, backtest all these approached to make your choice.
🧪Important: we used the long signals only below the zero-line and short signals above it in the attempt to catch the beginning of a trend and have large potential move. On the picture below you can see the same BITMART:BTCUSDT.P , but what will happen if we open long on the lines crossover above zero line? This trade will not be profitable because of restricted potential.
⚡️MACD Zero Line Crossover
Buy Signal:
MACD Histogram crosses above the zero line (momentum shifts from bearish to bullish)
Price closes above the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
Sell Signal:
MACD Histogram crosses below the zero line (momentum shifts from bullish to bearish)
Price closes below the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Wait until MACD Histogram crosses over zero line. Open long trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed above 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Take profit when price reaches 3:1 risk to reward ratio according to the stop-loss from point 4.
4. Stop-loss shall be placed below recent swing low. This point can be discussed, you can use any stop-loss technique described earlier in this article. We demonstrate the simplest one, the key here is using at least 3:1 RR.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Wait until MACD Histogram crosses under zero line. Open short trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed below 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Take profit when price reaches 3:1 risk to reward ratio according to the stop-loss from point 4.
4. Stop-loss shall be placed above recent swing high. This point can be discussed, you can use any stop-loss technique described earlier in this article. We demonstrate the simplest one, the key here is using at least 3:1 RR.
⚡️MACD Divergence Strategy
MACD Divergence is a strategy that helps traders identify potential reversals in market direction before they become obvious on the price chart. This makes it a favorite tool among swing traders and crypto enthusiasts looking to catch major moves early.
But what exactly is a divergence? In simple terms, divergence occurs when price and momentum (MACD) are moving in opposite directions — signaling that the current trend may be losing strength and preparing for a reversal. There are two main types of divergence.
🐂 Bullish Divergence
Price makes a lower low
MACD Histogram makes a higher low
This suggests that while price is still falling, downward momentum is weakening. The bears are losing control, and a bullish reversal may be near. Trading signal is very simple, when bullish divergence happens wait for the first increasing column on MACD histogram and open long trade. Place stop-loss under recent swing low and take profit at 3:1 RR.
🐻Bearish Divergence
Price makes a higher high
MACD makes a lower high
This suggests that while price is still falling, downward momentum is weakening. The bears are losing control, and a bullish reversal may be near. Trading signal is very simple, when bearish divergence happens wait for the first decreasing column on MACD histogram and open short trade. Place stop-loss above recent swing high and take profit at 3:1 RR.
🧪 Important hint: MACD histogram shall cross the zero line between two lows/high to create the most reliable divergence signals. We are not recommend to use it without zero-line crossover to decrease number of false signals.
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. MACD Histogram shall create higher low.
2. Price shall create lower low.
3. MACD Histogram shall cross the zero line between lows.
4. MACD Histogram shall show the first increasing column.
5. Put stop-loss under the recent swing low.
6. Put take profit at 3:1.
🧪 You can enhance the long signal with the MACD Line divergence. In our case we have both divergences: with MACD Histogram and MACD Line.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. MACD Histogram shall create lower high.
2. Price shall create higher high.
3. MACD Histogram shall cross the zero line between lows.
4. MACD Histogram shall show the first decreasing column.
5. Put stop-loss above the recent swing high.
6. Put take profit at 3:1.
🧪Divergence is extremely strong signal, but when price continue it's move in the direction of a trend and it's not reversing it can also be the signal for the trend continuation. This situation is called "Baskerville Hound" signal, this name was given by famous trader Alexander Elder. We don't recommend to use it for novice traders, but it's useful to know about it.
📚 Conclusion
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is more than just a crossover tool — it's a powerful momentum indicator that offers deep insight into the strength, direction, and timing of market trends. By understanding how the MACD line, Signal line, and Histogram interact, traders can uncover early trend shifts, spot momentum divergences, and time entries and exits with greater confidence.
Whether you're a short-term trader using fast crossovers for scalping or a long-term investor watching for weekly divergences, MACD can adapt to your style when used thoughtfully. Like all indicators, it works best when combined with price action, support/resistance levels, and other indicators — not in isolation.
Ultimately, mastering MACD is not about memorizing patterns, but about learning to read the story of momentum that unfolds beneath the surface of price. With disciplined application and practice, MACD can become a reliable compass in your trading strategy.
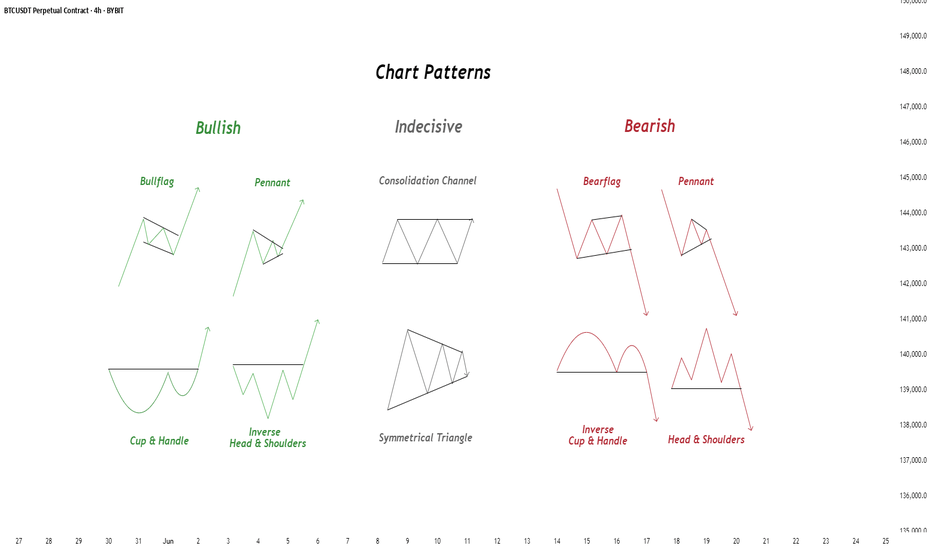
Chart Patterns - How to read them like a ProChart patterns are visual formations on price charts that help traders anticipate potential market movements.
These patterns fall into three main categories: bullish , bearish , and indecisive .
---
1. Bullish Chart Patterns
Bullish patterns often signal that price is likely to move upward.
1.1 Bull Flag
* What it looks like: A sharp upward move followed by a small downward-sloping rectangle (the flag).
* Meaning: After a strong rally, the price consolidates briefly before continuing higher.
* Key insight: A breakout above the flag typically signals a continuation of the trend.
1.2 Pennant (Bullish)
* What it looks like: A strong upward move followed by a small symmetrical triangle.
* Meaning: Similar to the bull flag, but the consolidation takes a triangular form.
* Key insight: Once price breaks above the pennant, the uptrend often resumes.
1.3 Cup & Handle
* What it looks like: A “U”-shaped curve (the cup) followed by a small downward drift (the handle).
* Meaning: This pattern suggests a period of accumulation before price breaks higher.
* Key insight: A breakout above the handle signals the beginning of a new bullish leg.
1.4 Inverse Head & Shoulders
* What it looks like: Three low points, with the middle low being the deepest.
* Meaning: This reversal pattern appears after a downtrend and signals a potential change to an uptrend.
* Key insight: A breakout above the “neckline” confirms the reversal.
---
2. Indecisive Chart Patterns
These patterns show market hesitation, where neither bulls nor bears are clearly in control.
2.1 Consolidation Channel
* What it looks like: Price moves within a horizontal channel.
* Meaning: Market is moving sideways with no strong trend.
* Key insight: A breakout in either direction often leads to a significant move.
2.2 Symmetrical Triangle
* What it looks like: Two converging trend lines forming a triangle.
* Meaning: This is a neutral pattern that can break out in either direction.
* Key insight: Traders wait for a breakout before taking a position.
---
3. Bearish Chart Patterns
Bearish patterns signal a high probability of downward price movement.
3.1 Bear Flag
* What it looks like: A sharp decline followed by a small upward-sloping rectangle.
* Meaning: After a strong drop, price consolidates before continuing lower.
* Key insight: A breakout below the flag suggests a continuation of the downtrend.
3.2 Pennant (Bearish)
* What it looks like: A sharp downward move followed by a small symmetrical triangle.
* Meaning: Similar to the bear flag, but the consolidation takes a triangular form.
* Key insight: A breakout downward typically resumes the bearish trend.
3.3 Inverse Cup & Handle
* What it looks like: An upside-down cup with a small upward drift forming the handle.
* Meaning: Indicates weakness after an uptrend, often followed by a drop.
* Key insight: A break below the handle usually signals a strong bearish move.
3.4 Head & Shoulders
* What it looks like: Three peaks, with the middle one being the highest.
* Meaning: A classic reversal pattern that indicates a potential shift from an uptrend to a downtrend.
* Key insight: A break below the “neckline” confirms the bearish reversal.
---
How to Use These Patterns
* Combine pattern recognition with support/resistance, volume, and indicators for stronger confirmation.
* Always wait for breakouts and avoid acting too early.
* Manage risk with stop-loss orders.
Take profit is more important than a stop lossAre you actually in profit, or just delaying your next loss?
How many times have you watched your gains vanish because you wanted more?
Maybe it's time to stop fearing losses and start planning exits.
Hello✌️
Spend 3 minutes ⏰ reading this educational material.
💸 Why Most Traders Lose Profits They Already Had
Most traders obsess over stop losses but never define where they'll take profits. Imagine entering a great trade, watching the price go up, then suddenly it pulls back and you're out with nothing. That happens because you didn’t define your win.
A well-placed take profit acts like a contract with your future self. It secures your gain before the market decides otherwise.
📉 No Take Profit? Say Hello to Unnecessary Losses
Failing to set a take profit is basically handing the market a free ticket to reverse your gains. Especially in the highly volatile crypto space, a missed exit often turns into a regretful stop out. So while everyone is talking about stop losses, you should focus on where the money is actually made.
🧮 A Clear Profit Target Creates a Clear Mind
Having a defined profit target gives your mind a place to rest. It brings structure and removes hesitation. This peace of mind is something new traders lack, which often leads them to close early or hold too long.
🧠 Greed Is the Real Enemy of Your Gains
Greed whispers "Wait, it might go higher"
But when you don't have a take profit plan, that whisper becomes your worst advisor. Pro traders map their exits before entering, while amateurs dream of riding forever.
🛡 True Capital Protection Begins with Profit Protection
If you're aiming for safe capital in crypto, it's not just about minimizing losses. It's about securing wins. Beginners often build their whole plan around stop loss. But advanced traders fear losing profits more than they fear taking a hit.
🎯 Take Profit Is Your Emergency Exit Plan
Setting a profit target is like having an escape route during a fire. Without it, you’ll panic when things turn. Crypto markets are full of pump traps. Your profit is only real when you actually take it.
🚪 Exit Strategy Matters More Than Entry
Everyone talks about entries, but it's your exit that defines whether your trade ends in green or red. Many traders nail the perfect entry but without a clear exit plan, they hand back their profits. Prioritizing your take profit is not optional. It’s essential.
🔁 Managing Gains Is Managing Emotions
Without a defined exit, every candle can shake your decision-making. But when your take profit is set in advance, emotions can’t hijack your strategy. You’re following a plan, not a feeling.
📊 TradingView Tools to Manage Take Profits Effectively
In the world of trading, the right tool means the right decision. TradingView offers powerful tools that help you manage not just your stop loss but more importantly, your take profit targets. With tools like Price Range and Long/Short Position, you can easily visualize where you entered and where you need to exit before greed pulls you deeper.
The Fibonacci Extension tool is especially valuable during bullish runs. It allows you to map out realistic and strategic profit levels like TP1, TP2, and TP3. These targets can then be paired with horizontal lines or alerts within TradingView’s chart system.
Even if you're using a free TradingView account, a simple custom Pine Script can help set alerts when your percentage targets are hit so you can scale out or lock in profits instead of emotionally reacting to price movement.
Using these tools practically empowers traders to build real-world strategies and take control of their exits, not just their entries. That’s the real edge.
📌 Final Takeaway
A clear, well-placed take profit protects both your money and your mind. Don’t let your wins dissolve into losses. With the right tools and the right mindset, you don’t just survive the market, you beat it. Start managing your profits today, not just your losses.
✨ Need a little love!
We pour love into every post your support keeps us inspired! 💛 Don’t be shy, we’d love to hear from you on comments. Big thanks , Mad Whale 🐋
📜Please make sure to do your own research before investing, and review the disclaimer provided at the end of each post.
Mechanical vs. Anticipation Trades: The Fine LineWhen traders talk about discipline, they often refer to following rules — sticking to a plan, being methodical, and avoiding emotional decisions. But there's a subtle and powerful difference between being rule-based and being blindly mechanical. And even more, there's a moment in every trader’s process where discipline demands adaptation.
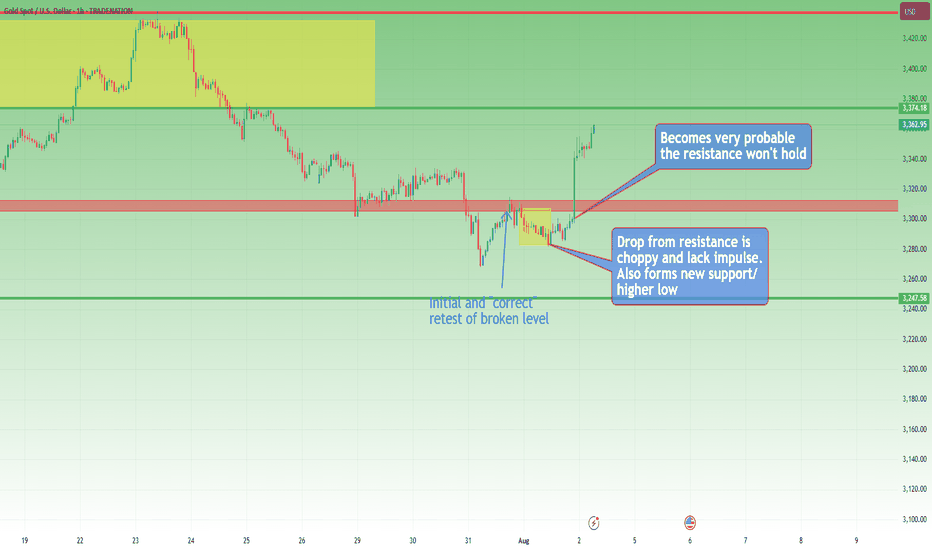
Let’s look at a recent trade on Gold to understand this better.
On Thursday, I published an analysis on Gold stating that the recent breakdown of support had turned that zone into resistance. A short entry from that level made sense.
It was mechanical, clean, and aligned with what the chart was showing at the time.
And, at first, it worked. Price rose into the resistance area and dropped. Perfect reaction. Textbook setup. Confirmation. The kind of trade you want to see when following a rule-based system.
But then something changed.
Price came back. Quickly.(I'm talking about initial 3315-3293 drop and the quick recover)
So, the very next rally pushed straight back into the same resistance area, hmmm...too simple, is the market giving us a second chance to sell?
That was the first sign that the market might not respect the previous structure anymore.
It dipped again after, but the second drop was different: slower, weaker, choppier.
That told me one thing: the selling pressure was fading.
So I shifted. From mechanical execution to anticipatory mindset.
This is where many traders struggle — not because they don’t have a system, but because they don’t know when to let go of it. Or worse: they abandon it too quickly without cause.
In this case, the evidence was building. The failed follow-through. The loss of momentum. The compression in structure. All signs that a reversal was brewing.
Rather than continuing to blindly short, referring to a zone that no longer held the same weight, I started looking for the opposite: an upside breakout and momentum acceleration.
That transition wasn’t based on emotion. It was based on market behavior.
________________________________________
Mechanical vs. Anticipation: What’s the Real Difference?
A mechanical trade is rule-based:
• If X happens, and Y confirms, then enter.
• No need for interpretation, no second guessing.
• It can (in theory) be automated.
An anticipatory trade is different:
• It’s about reading intent in price action before confirmation.
• Higher risk usually, but higher reward if you’re right.
• Can’t be automated. It requires presence, experience, and context.
And the tricky part? Often, we lie to ourselves. We say we’re "mechanical" while actually guessing. Or we think we’re being smart and intuitive, when in fact, we’re being impulsive.
The key is awareness.
In my Gold ideas, the initial short was mechanical. But the invalidation came quickly — and I was alert enough to switch gears. That shift is not a betrayal of discipline. It’s an upgrade of it.
________________________________________
Final Thoughts:
Discipline is not doing the same thing no matter what. Discipline is doing what the market requires you to do, without emotional distortion.
And that, often, means walking the fine line between the setup you planned for, and the reality that just showed up.
Disclosure: I am part of TradeNation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Simple Psychology Tips Using Volume for Better TradingMany newer traders assume that when someone says "psychology" in trading, they are referring to mindset.
It is also widely believed that trading is about the BEST entries.
Now, think of it this way. It is not about winning trades, it is actually about managing losses well to allow you to take the winners over and over again. You might think that a 3 to 1 risk-to-reward strategy is boring, you might have gone all in on your favourite crypto project. But what makes the difference between gambling and trading is actually very, very simple. So simple, in fact, many overlook it or simply ignore it.
Most seek a silver bullet - high win rates and perfectly timed entries, then they overleverage and move stops on the one "good trade" they are seeking to make.
Whilst doing this, they tend to overload the 6 monitors they have purchased to trade with a thousand indicators, which they don't really need.
The candlesticks tell a story, volume supports that story. When you learn any technique from Elliott Waves to Wyckoff, they all have a dependence on volume - even if the correlation is not apparent.
Look at this first image.
Price had moved down since the vertical line, the AD line also moved down - sell-off, in full swing. But then volume starts to shift before the AD line starts to increase.
Now, look at what happens next...
As we move forward and the new vertical line shows where volume spiked, the AD line starts to decrease as the price continues to rise.
This is enough of a story to start your analysis.
We then get a move with a lower high formed.
As this plays out, the sell-side volume rises, creating momentum for the short position.
Look a little closer and you will see, that the volume on the move up just before the drop was also decreasing. Making a divergence to price.
You might feel that the market is against you, or that the big players are single-handedly seeking your stops. But the truth is, the psychology in moves such as this one shown is where most retail traders either have greed that markets will only go up for ever or the fear that they are missing out on a market that only goes up forever.
It is that herd mentality that generates the liquidity for the professionals.
Losing 1% on a trade, is part of the process, risking 80%> on a single move will make you paper rich for about 10 minutes before the real losses set in.
This is where the psychology and the basic techniques such as risk management and understanding what candlesticks and volume bars are telling you, will make a world of difference to your results.
A/D line and volume are free on @TradingView and to be fair you don't need to overcomplicate it more than that!
Stay safe, have a great weekend all!!!
Disclaimer
This idea does not constitute as financial advice. It is for educational purposes only, our principal trader has over 25 years' experience in stocks, ETF's, and Forex. Hence each trade setup might have different hold times, entry or exit conditions, and will vary from the post/idea shared here. You can use the information from this post to make your own trading plan for the instrument discussed. Trading carries a risk; a high percentage of retail traders lose money. Please keep this in mind when entering any trade. Stay safe.
10 POWERFUL INVESTING & TRADING QUOTES OF ALL TIME
Here are powerful quotes of professional traders, investors and experts in financial markets.
Let their words inspire you and help you in your trading journey.
"To succeed in the market, you must learn to think like everyone else and do the opposite." - Sir John Templeton 📈💭💡
"The four most dangerous words in investing are: 'This time it's different.'" - Sir John Templeton ⏳📉🛑
"The more you learn, the more you earn." - Warren Buffett 📚💰📈
"The key to trading success is emotional discipline. If intelligence were the key, there would be a lot more people making money." - Victor Sperandeo. 💪💰🚫🧠
"Investing is not about making predictions, it's about having a plan and sticking to it." - Tony Robbins 📊🔄📌
"The best time to buy a stock is when the blood is running in the streets." - Baron Rothschild 💀🔪💰
"The best investment you can make is in yourself." - Warren Buffett 💼💡💰
"The stock market is not a casino; it's a crooked casino." - Charlie Munger 🎰🎲🏛️
"Losses are part of the game. You can't win every trade." - Martin Schwartz. 📉😔💔
"The fundamental law of investing is the uncertainty of the future." - Peter Bernstein. ⚖️❓🔮
The More I trade, the more I realize how precise and meaningful are these phrases. Take them seriously, and they will help you achieve the financial success.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
HOW TO TRADE THE TREND WITH THE 8-STAGE "MARKET TREND MODEL"How to TRADE THE TREND ,
and decide WHEN TO GO LONG OR SHORT ,
using 8-STAGE MARKET LIFECYCLE ROADMAP
This way you will INCREASE YOUR WIN RATE ,
avoid getting stopped out by BEING COMPLETELY AGAINST THE MARKET ,
while seeing BIG MISSED MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
The Methodology is:
1. Simple & Systematic - so it is easy to learn
2. Works across all Markets
3. Works across all Timeframes
4. Can be combined with existing methodologies..
DXY Top-Down Analysis: Market Structure & Directional Bias This video demonstrates a top-down analysis of DXY. I'll show you how to identify market structure, value areas, directional bias, and key support and resistance levels. You'll learn to analyze the market from weekly to hourly timeframes using Heikin-Ashi candles and the 200 EMA.
Fibonacci Arcs in Stock TradingFibonacci Arcs in Stock Trading
Fibonacci arcs, derived from the renowned Fibonacci sequence, offer a compelling blend of technical analysis and market psychology for traders. By mapping potential support and resistance areas through arcs drawn on stock charts, these tools provide insights into future price movements. This article delves into the practical applications of Fibonacci arcs in trading, their interplay with market psychology, and best practices for effective use.
Understanding Fibonacci Arcs
The Fibonacci arc indicator is a unique tool in technical analysis derived from the famed Fibonacci sequence. It’s crafted by drawing arcs at the key Fibonacci retracement levels - 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% - from a high to a low point on a stock chart. Each curve represents potential support or resistance areas, offering insights into the stock’s future movements.
The art of arc reading, meaning interpreting these curves, is crucial for traders. When a stock approaches or intersects with an arc, it reflects a significant reaction level. For instance, if a stock price touches or nears an arc, it could face arc resistance, indicating a potential halt or reversal in its trend.
Applying Fibonacci Arcs in Trading
In the stock market, these arcs serve as a guide for traders seeking to anticipate future price movements. When applied correctly, they can provide critical insights into potential support and resistance levels. Here's a step-by-step look at how you may use them effectively:
- Identifying High and Low Points: Begin by selecting a significant high and low point on the stock's chart. In an uptrend, it’s the most recent swing high to a previous swing low, and vice versa. These are the anchor points.
- Drawing the Arcs: Once the points are selected, draw the arcs at the Fibonacci retracement levels of 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%. They radiate from the chosen low point to the high point (or vice versa), cutting across the chart.
- Interpretation: Watch how the stock interacts with these lines. When the price approaches an arc, it might encounter resistance or support, signalling a potential change in trend or continuation.
- Timing Entries and Exits: Traders can use the arcs in the stock market as a tool to time their trading decisions. For instance, a bounce could be a signal to enter a trade, whereas the price breaking through might suggest it's time to exit.
Fibonacci Arcs and Market Psychology
The effectiveness of Fibonacci arcs in trading is deeply intertwined with market psychology. They tap into the collective mindset of traders, who often react predictably to certain price levels. The Fibonacci sequence, underlying this tool, is not just a mathematical concept but also a representation of natural patterns and human behaviour.
When a stock nears a curve, traders anticipate a reaction, often leading to a self-fulfilling prophecy. If many traders make an arc stock forecast, they might sell as the price approaches a certain point, causing the anticipated resistance to materialise. Similarly, seeing support at an arc can trigger buying, reinforcing the tool’s power.
This psychological aspect makes Fibonacci arcs more than just technical tools. They are reflections of the collective expectations and actions of market participants, turning abstract mathematical concepts into practical indicators of market sentiment and potential movements.
Best Practices
Incorporating Fibonacci arcs into trading strategies involves nuanced techniques for better accuracy and efficacy. Here are some best practices typically followed:
- Complementary Tools: Traders often pair this tool with other indicators like moving averages or RSI for a more robust analysis.
- Accurate Highs and Lows: It's best to carefully select the significant high and low points, as the effectiveness of the curves largely depends on these choices.
- Context Consideration: Understanding the broader market context is crucial. Traders usually use Fibonacci arcs in conjunction with fundamental factors to validate their analysis.
- Watch for Confluence: Identifying areas where Fibonacci levels converge with other technical signals can provide stronger trade setups.
- Practice Patience: Traders typically avoid making hasty decisions based solely on Fibonacci levels. It's usually better to wait to see additional confirmation from the price action.
Advantages and Limitations of Fibonacci Arcs
Fibonacci arcs are a popular tool in technical analysis, offering distinct advantages and some limitations in analysing stock movements. Understanding these can help traders leverage the tool more effectively.
Advantages
- Intuitive Nature: The Fibonacci sequence is a natural pattern, making the tool intuitive for traders to understand and apply.
- Dynamic Support and Resistance Levels: They provide dynamic levels of support and resistance, unlike static lines, adapting to changing market conditions.
- Versatility: Effective in various market conditions, the arcs can be used in both trending and sideways markets.
Limitations
- Subjectivity in Selection: The effectiveness largely depends on correctly identifying the significant high and low points, which can be subjective.
- Potential False Signals: Like all technical tools, they can generate false signals, especially in highly volatile markets.
- Requires Complementary Analysis: To maximise effectiveness, these curves are usually used alongside other technical indicators, as they are not infallible on their own.
The Bottom Line
Fibonacci arcs are invaluable tools in stock analysis, providing insights into market trends and potential price movements.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
14-Day Mindset Challenge: Become a Top Trader — Day 114 Days. Challenge: How to Become a Mindset-Strong Trader
Day 1: The Power of Physical Exercise in Enhancing Trading Performance
Embarking on a trading journey demands more than just technical knowledge and market analysis; it requires a resilient and focused mindset. One often overlooked but incredibly powerful tool to develop this mental strength is physical exercise. Regular movement not only benefits your body but also profoundly influences your mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall performance as a trader.
When you engage in physical activity, your brain releases a cascade of chemicals that improve mood, focus, and resilience—crucial qualities for navigating the volatile world of trading. Think of your body and mind as interconnected systems: by strengthening your physical health, you lay a solid foundation for a sharper, more disciplined trading mindset. Over the next 14 days, committing to a simple, consistent exercise routine can transform how you approach your trading sessions, helping you stay calm under pressure, make better decisions, and recover quickly from setbacks.
Let's start!
How Physical Exercise Improves Your Trading Results
1. Boosts Endorphin Production for Positive Feelings
One of the most immediate benefits of exercise is the release of endorphins—natural chemicals that promote feelings of happiness and reduce stress and pain. This positive mood boost helps traders maintain a calm and focused mindset, even amidst market volatility. Scientific studies have shown that regular physical activity increases endorphin levels, which can combat anxiety and improve overall emotional resilience.
2. Enhances Insulin Activity and Energy Levels
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, enabling your body to more efficiently process glucose for energy. This increased metabolic efficiency helps combat fatigue and sustains mental alertness during prolonged trading sessions. Research indicates that physically active individuals experience higher energy levels and better stamina, which are vital for maintaining attention and decision-making capacity.
3. Reduces Disease Risk and Promotes Long-Term Health
Regular physical activity reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other chronic health issues. By maintaining good health, traders are less likely to experience unexpected absences due to illness and can trade consistently over time. Scientific evidence supports that healthier individuals have better cognitive function and emotional stability, both crucial for trading success.
4. Boosts Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Exercise increases heart rate and blood flow, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the brain. Numerous studies have demonstrated that physical activity stimulates the growth of new neural connections and enhances neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and learn. This leads to improved memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills, all essential for analyzing markets and executing trades efficiently.
5. Enhances Stress Regulation and Emotional Control
Research shows that regular exercise helps regulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls stress responses. By improving your body’s ability to handle stress, exercise reduces the likelihood of emotional reactions such as impulsivity or panic during trading. This emotional regulation is key to maintaining discipline and sticking to your trading plan under pressure.
6. Improves Sleep Quality
Quality sleep is fundamental for cognitive performance and emotional regulation. Scientific studies have consistently shown that physical activity, especially aerobic exercise, improves sleep quality and duration. Better sleep enhances focus, decision-making, and emotional resilience—traits that directly impact trading performance.
7. Promotes Neurotransmitter Balance
Exercise influences the production and regulation of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. These chemicals play a vital role in mood, motivation, and alertness. Balanced neurotransmitter levels support a positive mindset, resilience to setbacks, and sustained motivation—key ingredients for consistent trading.
8. Increases Resilience to Market Stressors
Finally, regular physical activity builds overall resilience—both physically and mentally. This resilience helps traders recover quickly from losses, handle unexpected market shocks, and stay committed to their strategies without succumbing to frustration or panic.
Incorporating these scientifically-backed points emphasizes how exercise not only benefits physical health but also fundamentally enhances the mental and emotional capacities critical for successful trading.
Taking Action: Your 14-Day Exercise Implementation Plan
1. Decide Your Exercise Routine
Choose activities that you enjoy and can commit to every day for the next two weeks. Whether it’s walking, jogging, weightlifting, yoga, Pilates, push-ups, mountain climbers, or any other physical activity—what matters is consistency. Pick something that makes you feel energized and motivated.
2. Set a Daily Time Commitment
Determine how much time you can dedicate each day—start with 30 minutes to 1 hour. Make it a non-negotiable part of your daily schedule. For example, you might decide to go for a brisk walk in the morning, do bodyweight exercises at home, or hit the gym. The goal is to establish a routine that becomes a natural part of your day.
3. Use Reminders and Push Through Initial Discomfort
Especially during the first two weeks, it’s normal to feel some resistance or emotional stress about starting new habits. Set reminders on your phone or calendar to prompt you. Be patient and persistent—initial discomfort will fade as your body adapts. Once exercise becomes a habit, it will feel less like a chore and more like a source of strength.
Final Tips for Success
Start Small, Progress Gradually: Don’t overcommit at the beginning; build gradually to avoid burnout.
Stay Consistent: Consistency beats intensity—daily effort compounds over time.
Track Your Progress: Keep a journal or use an app to monitor your activity and observe how you feel over the days.
Enjoy the Process: Find joy in the movement itself. As it becomes part of your routine, you'll notice improvements not only physically but also in your trading mindset.
Conclusion
A 14-day commitment to physical exercise can be a game-changer for your trading mindset. By boosting endorphins, increasing energy, enhancing brain function, and reducing health risks, you set the stage for more disciplined, confident, and resilient trading. Embrace this challenge—your mind and your portfolio will thank you.
✅ Follow me and save this educational post: "14-Day Mindset Challenge: Become a Top Trader — Day 1". Tomorrow, I'll be releasing Day 2 of the transformation... Stay tuned!
✅ Please share your thoughts about this article in the comments section below and HIT LIKE if you appreciate my post. Don't forget to FOLLOW ME; you will help us a lot with this small contribution.
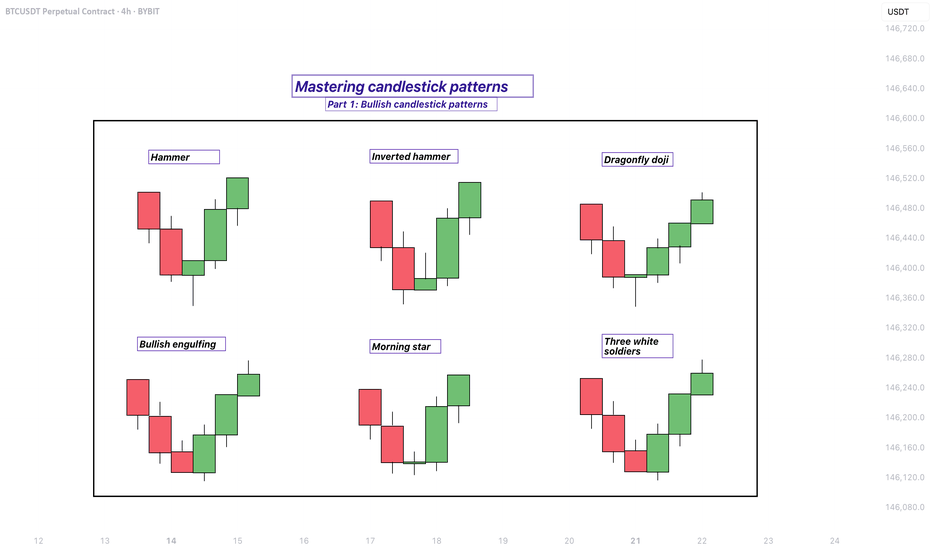
Mastering bullish candlestick patterns - How to use it!In this guide, we will explore some of the most important bullish candlestick patterns used in technical analysis. These patterns are essential tools for traders and investors who want to better understand market sentiment and identify potential reversal points where prices may start moving upward.
What will be explained:
- What are bullish candlestick patterns?
- What is the hammer?
- What is the inverted hammer?
- What is the dragonfly doji?
- What is the bullish engulfing?
- What is the morning star?
- What is the three white soldiers?
- How to use bullish candlestick patterns in trading?
What are bullish candlestick patterns?
Bullish candlestick patterns are specific formations on a candlestick chart that signal a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend. These patterns are used by traders and investors to identify moments when the market sentiment may be shifting from bearish to bullish. Recognizing these patterns can help traders time their entries and make more informed decisions based on price action and market psychology. While no single pattern guarantees success, they can provide valuable clues when combined with other forms of analysis such as support and resistance, trendlines, and volume.
What is the Hammer?
The Hammer is a single-candle bullish reversal pattern that typically appears at the bottom of a downtrend. It has a small real body located at the upper end of the trading range, with a long lower shadow and little to no upper shadow. The long lower wick indicates that sellers drove the price lower during the session, but buyers stepped in strongly and pushed the price back up near the opening level by the close. This shift in momentum suggests that the downtrend could be coming to an end, and a bullish move might follow.
What is the Inverted Hammer?
The Inverted Hammer is another single-candle bullish pattern that also appears after a downtrend. It has a small body near the lower end of the candle, a long upper shadow, and little to no lower shadow. This pattern shows that buyers attempted to push the price higher, but sellers managed to bring it back down before the close. Despite the failure to hold higher levels, the buying pressure indicates a possible reversal in momentum. Traders usually look for confirmation in the next candle, such as a strong bullish candle, before acting on the signal.
What is the Dragonfly Doji?
The Dragonfly Doji is a special type of candlestick that often indicates a potential bullish reversal when it appears at the bottom of a downtrend. It forms when the open, high, and close prices are all roughly the same, and there is a long lower shadow. This pattern shows that sellers dominated early in the session, pushing prices significantly lower, but buyers regained control and drove the price back up by the end of the session. The strong recovery within a single period suggests that the selling pressure may be exhausted and a bullish reversal could be imminent.
What is the Bullish Engulfing?
The Bullish Engulfing pattern consists of two candles and is a strong indication of a reversal. The first candle is bearish, and the second is a larger bullish candle that completely engulfs the body of the first one. This pattern appears after a downtrend and reflects a shift in control from sellers to buyers. The bullish candle’s large body shows strong buying interest that overpowers the previous session’s selling. A Bullish Engulfing pattern is even more significant if it occurs near a key support level, and it often signals the beginning of a potential upward move.
What is the Morning Star?
The Morning Star is a three-candle bullish reversal pattern that occurs after a downtrend. The first candle is a long bearish one, followed by a small-bodied candle (which can be bullish, bearish, or a doji), indicating indecision in the market. The third candle is a strong bullish candle that closes well into the body of the first candle. This formation shows a transition from selling pressure to buying interest. The Morning Star is a reliable signal of a shift in momentum, especially when confirmed by high volume or a breakout from a resistance level.
What is the Three White Soldiers?
The Three White Soldiers pattern is a powerful bullish reversal signal made up of three consecutive long-bodied bullish candles. Each candle opens within the previous candle’s real body and closes near or at its high, showing consistent buying pressure. This pattern often appears after a prolonged downtrend or a period of consolidation and reflects strong and sustained buying interest. The Three White Soldiers suggest that buyers are firmly in control, and the market may continue moving upward in the near term.
How to use bullish candlestick patterns in trading?
To effectively use bullish candlestick patterns in trading, it’s important not to rely on them in isolation. While these patterns can signal potential reversals, they work best when combined with other technical tools such as support and resistance levels, moving averages, trendlines, and volume analysis. Traders should also wait for confirmation after the pattern forms, such as a strong follow-through candle or a break above a resistance level, before entering a trade. Risk management is crucial—always use stop-loss orders to protect against false signals, and consider the broader market trend to increase the probability of success. By integrating candlestick analysis into a comprehensive trading strategy, traders can improve their timing and increase their chances of making profitable decisions.
Thanks for your support. If you enjoyed this analysis, make sure to follow me so you don't miss the next one. And if you found it helpful, feel free to drop a like 👍 and leave a comment 💬, I’d love to hear your thoughts!
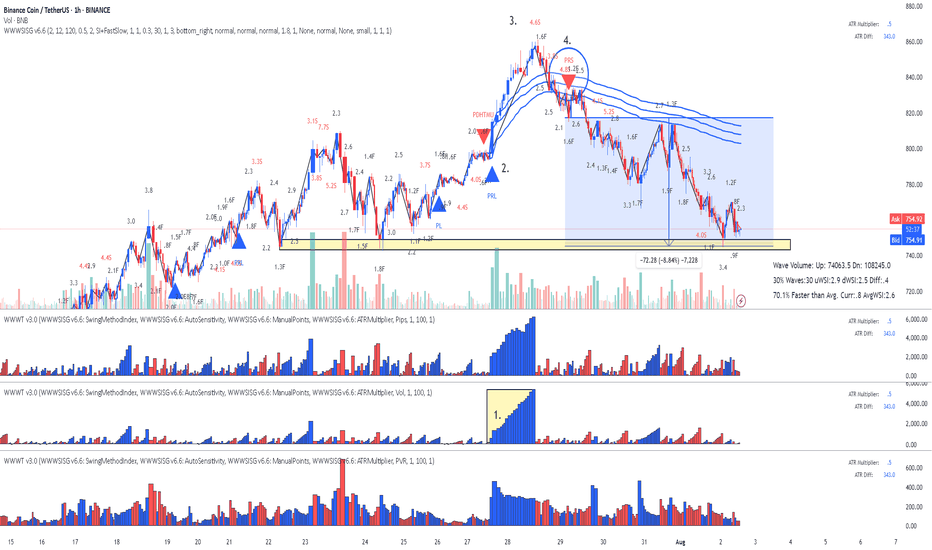
BNB Binance Coin: Lesson 15 methodology did the job again
Lesson 15 methodology (annotations in sync with the chart):
1. Largest up volume wave after a while - sellers might be in there.
2. Placed AVWAP and waited for price to cross downwards and pullback again on AVWAP
3. HTMU (hard to move up) - Abnormal Speed Index 4.6S at the top
4. Entry short signal PRS with abnormal SI 4.8.2 (price has a hard time to move up - absorption)
Simple as that. Enjoy!
Stock Allocation IdeasIf you're building a stock portfolio, how you allocate your money matters as much as what you buy. Here’s a practical, risk-aware approach for retail traders and investors:
1. Core and Satellite Approach
Core (60–70%): Stick with strong, stable companies—large-cap names with reliable earnings like AAPL, MSFT, or JNJ. These form the foundation of your portfolio.
Satellite (30–40%): Use this portion for high-potential ideas—growth stocks, emerging tech (like AI or EV), or small caps. Higher risk, but higher potential return.
2. Mix Between Defensive and Growth Stocks
In volatile markets, lean toward defensive sectors (healthcare, consumer staples, utilities).
In bull markets or improving conditions, increase exposure to growth sectors (tech, consumer discretionary).
3. Blend Growth and Value
Balance high-growth stocks with undervalued, stable companies.
When interest rates are high or inflation is rising, value stocks often perform better.
When rates fall or the economy picks up, growth stocks usually lead.
4. Don't Ignore International Exposure
While U.S. stocks are strong, consider adding 20–30% exposure to global markets (Europe, Japan, or select emerging markets).
5. Stay Disciplined with Rebalancing
Check your portfolio every 3 months.
Take profits where gains have outpaced, and reinvest in areas that are still fundamentally strong but lagging.
Final Tip: Focus on position sizing and risk management. You don’t need to hit every trade—preserving capital and staying in the game is the priority.
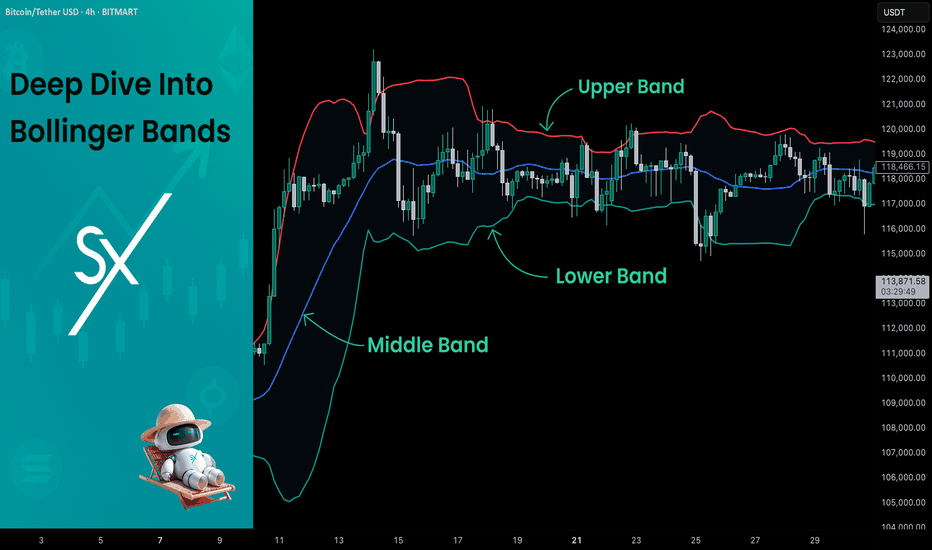
Deep Dive Into Bollinger Bands 🗓This article explores the Bollinger Bands indicator—a powerful volatility tool used by traders worldwide. You'll learn how it works, how to calculate it, and how to use it to detect potential breakouts, trend reversals, and overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
📚 Introduction to Bollinger Bands
In the fast-paced world of trading, understanding market volatility is key to making informed decisions. Bollinger Bands, developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, offer a visual and statistical method to measure this volatility. Unlike simple moving averages, which only tell you the trend, Bollinger Bands expand and contract based on recent price action, helping traders spot overbought, oversold, or consolidation phases.
These bands dynamically adjust to market conditions, making them one of the most popular indicators for trend-following, mean-reversion, and breakout strategies. Whether you’re trading crypto, stocks, or forex, Bollinger Bands can help you identify high-probability setups by combining trend direction with volatility.
📚 How Bollinger Bands Are Calculated
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines:
Middle Band – This is a simple moving average (SMA) of the price, typically over 20 periods.
Upper Band – The middle band plus two standard deviations.
Lower Band – The middle band minus two standard deviations.
Middle Band = SMA(n)
Upper Band = SMA(n) + (k × σₙ)
Lower Band = SMA(n) - (k × σₙ)
Where σₙ is the standard deviation of the price for n periods and k is the multiplier, typically set to 2, which captures ~95% of price action under normal distribution. The middle band shows the average price over the last 20 candles. The upper and lower bands adjust based on how volatile the price has been — expanding in high volatility and contracting in low volatility.
🤖 For those traders who want to implement Bollinger Bands into algorithmic strategy we provide formula it's calculation in Pine Script:
basis = ta.sma(src, length) // Middle Band (SMA)
dev = mult * ta.stdev(src, length) // Standard Deviation × Multiplier
upper = basis + dev // Upper Band
lower = basis - dev // Lower Band
📚 How to Use MACD in Trading Strategies
⚡️Bollinger Band Squeeze (Volatility Contraction and Expansion)
The idea is pretty simple, а squeeze indicates low volatility and often precedes a breakout. The squeeze is the situation when the Upper Band and Lower Band contract, and BB width is at a local minimum. In this case you shall be prepared for the high volatility after the period of low volatility. This strategy doesn’t predict direction — it prepares you for volatility.
Long setup:
Price is in long-term uptrend, you can use 200 EMA as a major trend approximation - price shall be above it.
Bollinger Bands is narrow in comparison to the previous period. Price usually is in sideways.
Open long trade when candle shows a breakout and closes above the Upper Band.
Set a trailing stop-loss at the Middle Band.
Short setup:
Price is in long-term downtrend, you can use 200 EMA as a major trend approximation - price shall be below it.
Bollinger Bands is narrow in comparison to the previous period. Price usually is in sideways.
Open short trade when candle shows a breakdown and closes below the Lower Band.
Set a trailing stop-loss at the Middle Band
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Price candle shall be closed above 200-period EMA. In our example we have BITMART:BTCUSDT.P 4h time frame.
2. Bollinger Bands shall be narrow in comparison with the previous periods.
3. Open long trade when candle closes above the Upper Band.
4. Close trade when price touched the Middle Band.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Price candle shall be closed below 200-period EMA. In our example we have BITMART:BTCUSDT.P 4h time frame.
2. Bollinger Bands shall be narrow in comparison with the previous periods.
3. Open short trade when candle closes below the Lower Band.
4. Close trade when price touched the Middle Band.
⚡️Mean Reversion (Rebound from the Bands)
This is the most common approach to use Bollinger Bands. The idea is also very simple, we just want to open long if price touches Lower Band and short if price reaches Upper Band. Price tends to revert to the mean (Middle Band), especially in range-bound markets. It's very important to trade in the direction of the major trend to reduce the probability of the large move against you.
Long setup:
Price is in long-term uptrend, you can use 200 EMA as a major trend approximation - price shall be above it.
Open long trade when price touches the Lower Band.
Set the initial stop-loss at the fixed percentage below entry price. Choose this percentage number with your personal risk/money management, you shall be comfortable to lose this amount of money in case of stop-loss hit.
If price reached Middle Band set stop-loss at breakeven.
Close trade when price reached the Upper Band.
Short setup:
Price is in long-term downtrend, you can use 200 EMA as a major trend approximation - price shall be below it.
Open short trade when price touches the Upper Band.
Set the initial stop-loss at the fixed percentage above entry price. Choose this percentage number with your personal risk/money management, you shall be comfortable to lose this amount of money in case of stop-loss hit.
If price reached Middle Band set stop-loss at breakeven.
Close trade when price reached the Lower Band.
🧪 Important: the most common approach to close trades is the Middle Band touch, this is classic mean reversion. We experimented multiple times with different approached and revealed that usually it's better to take profit at the Upper/Lower band for long/short trades and use Middle Band only for setting stop-loss at breakeven. This approach provides better risk to reward ratio.
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Price candle shall be closed above 200-period EMA. In our example we have BITMART:BTCUSDT.P 4h time frame.
2. Open long trade the Lower Band.
3. Put Initial stop-loss 2% below the entry price.
4. When price reached Middle band place stop-loss at the breakeven.
5. Close long trade at the Upper Band.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Price candle shall be closed below 200-period EMA. In our example we have BITMART:BTCUSDT.P 4h time frame.
2. Open short trade the Upper Band.
3. Put Initial stop-loss 2% above the entry price.
4. When price reached Middle band place stop-loss at the breakeven.
5. Close short trade at the Lower Band.
🧪 Important tip: notice that initial stop-loss is needed only to avoid disaster in case of price moves strongly against you. This percentage shall give enough space to avoid its reaching too often. Mean reversion strategy provides fast trades with the small average gain, so you shall maintain the high win rate (perfectly above 70%). You have to choose stop-loss based on particular asset volatility.
⚡️Combined Approach: Mean Reversion + Trend Following
Skyrexio made multiple researches about Bollinger Bands strategies and we found that we can receive better gains in combination of different approaches. Mean reversion gives you great entry with discount but you don't need to exit that early. Use the trading stop and allow to gain profit while market is moving in your direction.
This approach you can find in our advanced strategy Bollinger Bands Enhanced Strategy which we shared in 2024. Click on the link to read about it and understand how you can combine best features of this popular indicator.
📚 Conclusion
Bollinger Bands are more than just a volatility indicator — they provide a flexible framework for understanding price dynamics and market conditions. By visualizing the relationship between price and standard deviation around a moving average, traders can gain valuable insights into whether an asset is consolidating, trending, or preparing for a breakout.
The real strength of Bollinger Bands lies in their versatility. They can adapt to different trading styles — whether you’re a short-term scalper, a swing trader, or a long-term position holder. From identifying squeeze setups to riding strong trends or capturing mean reversion moves, BBs offer a strategic edge when used correctly.
However, Bollinger Bands should never be used in isolation. Like any technical tool, they work best when combined with momentum indicators like RSI or MACD, volume analysis, and price action signals. Context is key: a signal that works well in a ranging market may fail during high momentum trends.
Ultimately, Bollinger Bands help traders make more informed, disciplined decisions by clarifying where price stands relative to recent history. When paired with sound risk management and broader market awareness, they become a powerful ally in navigating market uncertainty.
Learning#04 : PDH & PDL🎯 Learning#04 : PDH & PDL
- The 2 Levels Every Intraday Trader Must Watch
Turn Yesterday’s Levels into Today’s Profits – PDH/PDL Playbook
In intraday trading, simplicity often beats complexity.
You don’t always need fancy indicators, dozens of lines, or complicated systems. Sometimes, two levels are all it takes to stay in sync with the market:
👉 Previous Day’s High (PDH)
👉 Previous Day’s Low (PDL)
These levels may look basic, but they carry psychological weight and often mark where real action — and opportunity — unfolds.
Let’s break it down into a practical strategy you can start using as early as tomorrow morning 👇
🧠 What Are PDH and PDL?
PDH = The highest price the market reached yesterday
PDL = The lowest price the market reached yesterday
That’s it. No calculations. No indicators. Just two simple levels from the previous session.
But here’s why they matter:
They’re visible to everyone — retail traders, institutional desks, even algo systems. These are “memory zones” where the market often reacts — bouncing, breaking, or trapping traders in fakeouts.
Think of them as psychological boundaries.
When price approaches these levels, traders ask:
“Will it break or bounce?”
That hesitation — that moment of decision — is your opportunity.
⚡ Why These Levels Work So Well
✅ They’re objective — no subjectivity involved. Anyone can mark them.
✅ They’re reaction zones — price often stalls, breaks, or rejects here.
✅ They reflect sentiment — how price behaves around them reveals market strength or weakness.
PDH and PDL often act like turning points — or springboards for continuation. The key is in reading how price behaves when it gets there.
📊 3 Smart Ways to Trade Around PDH/PDL
Let’s look at three powerful setups based on how price behaves near these levels:
1️⃣ Rejection at PDH or PDL (Classic Reversal)
This is the simplest setup — and one of the most effective.
When price tests PDH or PDL but fails to break, it often leaves signs:
Long upper/lower wicks
Rejection candles (like pin bars or inside bars)
Sudden volume drop
💡 Example:
Nifty rallies to PDH at 22,180, prints a long upper wick, then forms a red candle closing below. That’s a reversal clue.
You could enter short below the rejection candle, with a stop just above the high and a target near VWAP or mid-range.
🎯 Why this setup works: Tight risk. Logical context. High clarity.
2️⃣ Breakout and Retest (Trend Continuation)
If price breaks through PDH/PDL with strength, don’t chase it.
Wait for price to pull back and retest the level.
If PDH was broken, wait for a bullish retest — former resistance becomes support.
If PDL was broken, wait for a bearish retest — former support becomes resistance.
💡 Example:
BankNifty breaks PDH, pulls back, then prints a bullish engulfing candle right at the level — confirmation to go long.
📌 This setup works best on trending days and offers cleaner entries than chasing breakouts.
3️⃣ The Failed Breakout (Trap Setup)
One of the most high-probability setups — and one that traps many.
Here’s how it plays out:
Price breaks PDH/PDL
But immediately snaps back inside the range
Traders who chased the breakout are now trapped
💡 Signal to watch:
A candle closes above PDH, followed by a candle that closes back below — that’s your short signal. Reverse for long setups around PDL.
🚨 Even more effective when the breakout happens on low volume — no real conviction behind the move.
🔧 Tools That Amplify These Setups
These setups work great with a clean chart — but a few tools can boost your edge:
VWAP: Check if price is extended or supported near PDH/PDL. When VWAP aligns with these levels — confluence zone!
Candlestick patterns: Look for pin bars, inside bars, or engulfing patterns at the level.
Opening range: If price breaks PDH/PDL early in the day,
especially within the first 30 minutes, it signals directional intent.
Volume: Strong breakouts need volume. Weak volume = likely fakeout.
🔑 Remember: You don’t trade the level — you trade the reaction at the level.
✅ Why This Simple Strategy Works
Don’t underestimate the power of PDH and PDL. These levels:
Show where emotions exist — greed and fear often play out here.
Create natural reaction zones — ideal spots for clean entries and exits.
Let you trade with structure, not guesswork.
Instead of chasing price all day, do this:
Mark PDH and PDL
Wait for price to approach the zone
Watch how it behaves
React with a plan — not emotion
✨ Simple, repeatable, and highly effective — if you stay patient and disciplined.
✍️ Final Thoughts
In a world full of overcomplicated strategies, PDH/PDL trading is a refreshing reminder that clarity often comes from simplicity.
These levels won’t give you 10 trades a day — but they will give you high-quality, context-driven opportunities that align with how real price and volume work.
See you in the next one — and until then:
Keep it simple. Trade with structure. Trust the levels.
— Kiran Zatakia
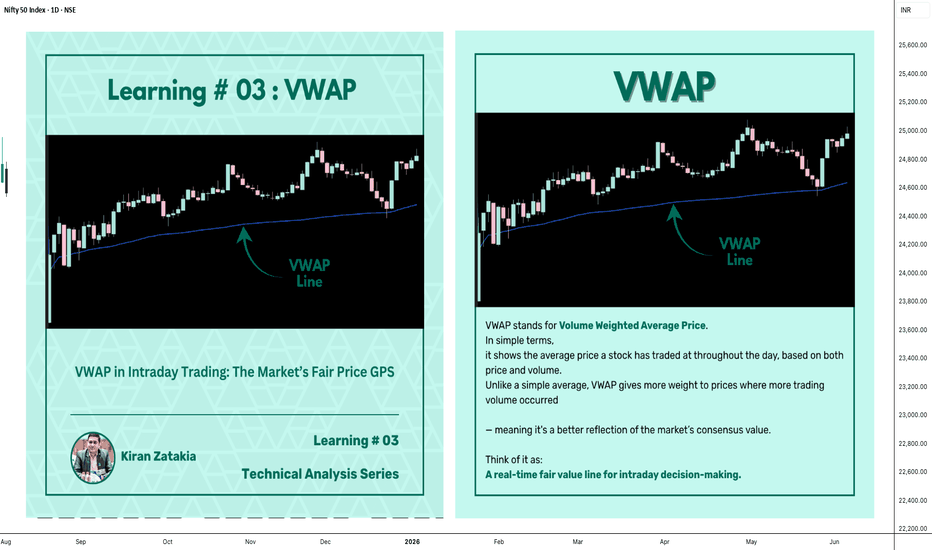
Learning#03 : VWAP in Intraday TradingLearning#03 : VWAP in Intraday Trading
📊 VWAP in Intraday Trading: The Market’s Fair Price GPS
Ever wondered if there’s a level that shows where the real trading action is happening? That’s exactly what VWAP does — it’s like a volume-weighted compass that intraday traders use to orient themselves in the market.
It’s not just another line on your chart. VWAP reflects where institutions and volume-heavy participants are active. That’s why understanding how price interacts with it can give you a serious edge.
Let’s break it down 👇
🧠 What is VWAP?
VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price.
In simple terms, it shows the average price a stock has traded at throughout the day, based on both price and volume.
Unlike a simple average, VWAP gives more weight to prices where more trading volume occurred — meaning it's a better reflection of the market’s consensus value.
Think of it as:
A real-time fair value line for intraday decision-making.
📈 Why VWAP Matters for Intraday Traders
VWAP acts as an intraday anchor. It tells you whether the price is currently trading above or below the day’s volume-weighted average — giving you quick insight into who's in control.
Here’s how to interpret it:
When price is above VWAP, buyers are in control and the bias is bullish.
When price is below VWAP, sellers are dominating and the bias is bearish.
When price is hovering near VWAP, the market is undecided, consolidating, or lacking direction.
In short, VWAP tells you who’s winning the intraday tug of war — and whether it’s even worth stepping in.
⚙️ How to Use VWAP in Your Intraday Strategy
1️⃣ VWAP as a Trend Filter
Before entering a trade, check where price is relative to VWAP:
Price above VWAP with higher lows → Focus on long setups
Price below VWAP with lower highs → Focus on short setups
🔁 Skip counter-trend trades. Stay with the flow.
This helps in trending markets by keeping you aligned with momentum.
2️⃣ VWAP as Dynamic Support or Resistance
VWAP behaves like a magnet. Price often pulls back to it and either:
Rejects (respects the level as support/resistance), or
Breaks and reclaims (signaling a potential reversal)
Use it alongside:
Flag patterns
Inside bars
Break-and-retest structures
3️⃣ VWAP Reversion Play (Snapback Trade)
This is a mean-reversion setup:
Price moves quickly away from VWAP at open
No strong follow-through, signs of exhaustion
Take a counter-trend trade back to VWAP
⚠️ Avoid this in strong trending markets — best used in choppy or fading environments.
4️⃣ VWAP with Price Action for Structure
Pair VWAP with clean price action:
Mark support and resistance zones
Observe price behavior near VWAP
Look for confirmation: inside bars, rejection wicks, engulfing candles
🎯 This adds logic and clarity to your entries — no random trades.
🔍 Bonus VWAP Tips
Combine VWAP with:
CPR (Central Pivot Range) for confluence zones
Opening range for breakout bias
Volume profile to spot high interest areas
These combos create strong, repeatable trade setups.
✅ VWAP Recap: Why It Matters
Here’s a quick breakdown of how VWAP can sharpen your intraday trading game:
Bias Building: VWAP helps confirm whether the market structure is bullish or bearish, giving you a reliable directional bias.
Trend Filtering: It keeps you aligned with the current momentum by filtering out counter-trend trades.
Pullback Entries: VWAP acts as a dynamic support or resistance level, offering clean zones to enter trades during pullbacks.
Mean Reversion: In sideways or fading markets, VWAP becomes a natural magnet — allowing you to target price reversions.
Risk Management: It provides logical reference points for placing stop-losses and defining entry zones, adding clarity to your risk-reward planning.
✍️ Final Thoughts
VWAP may sound simple, but it brings real structure to intraday trading.
It tells you where volume met price, and that’s powerful. When used with price action, it creates a solid framework for:
Building directional bias
Finding clean entries
Managing risk like a pro
VWAP doesn’t predict — it reflects. And in trading, reflection is more useful than prediction.
🛎️ Respect VWAP. Trade with structure.
— Kiran Zatakia
How to Use Engulfing Candles in TradingViewEngulfing patterns are among the most powerful candlestick formations because they signal strong momentum shifts and can help you spot dramatic trend reversal opportunities.
What You'll Learn:
• How to identify valid engulfing formations where one candle completely covers another's body
• The two types: bullish engulfing (green candle engulfs red) and bearish engulfing (red candle engulfs green)
• Psychology behind engulfing patterns: when one side completely overwhelms the other
• Using volume analysis to confirm engulfing pattern validity
• Finding meaningful engulfing patterns at trend highs and lows for reversal setups
• Timeframe considerations for engulfing analysis on any chart period
• Step-by-step trading strategy for engulfing reversal setups
• Setting proper stop losses above engulfing candle highs
• Determining profit targets below engulfing candle lows
• Managing wide-range drawdowns common with strong momentum shifts
• Advanced entry technique: waiting for retracements to improve risk-reward ratios
This tutorial may help futures traders and technical analysts who want to use powerful candlestick patterns to identify significant momentum changes.
The strategies covered could assist you in creating effective reversal setups when strong buying or selling pressure appears at key price levels.
Learn more about futures trading with Tradingview: optimusfutures.com
Disclaimer:
There is a substantial risk of loss in futures trading. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Please trade only with risk capital. We are not responsible for any third-party links, comments, or content shared on TradingView. Any opinions, links, or messages posted by users on TradingView do not represent our views or recommendations. Please exercise your own judgment and due diligence when engaging with any external content or user commentary.
This video represents the opinion of Optimus Futures and is intended for educational purposes only. Chart interpretations are presented solely to illustrate objective technical concepts and should not be viewed as predictive of future market behavior. In our opinion, charts are analytical tools—not forecasting instruments. Market conditions are constantly evolving, and all trading decisions should be made independently, with careful consideration of individual risk tolerance and financial objectives.
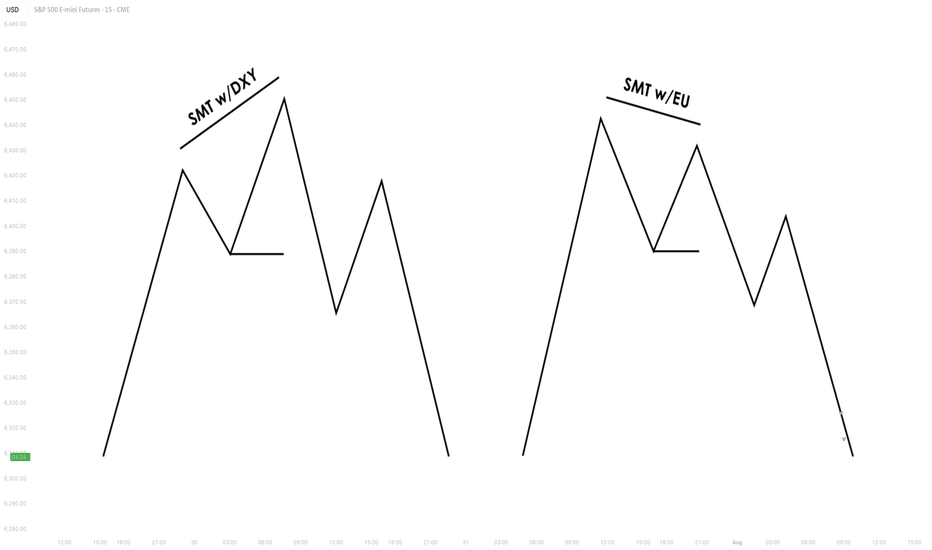
Understanding SMT Divergence In Trading1. Definition and Importance
SMT (Smart Money Technique) Divergence refers to a trading concept that involves identifying discrepancies between the price movement of correlated markets or instruments.
These discrepancies can signal potential market reversals or price manipulation. Specifically, it focuses on the divergence between price movements and indicators (like volume, momentum, or oscillators) in markets that typically move in sync.
In SMT Divergence, traders look for situations where two or more correlated instruments (like
Forex pairs, indices, or bonds) are moving in opposite directions. This "divergence" signals that
there may be a shift in market sentiment, liquidity manipulation, or an opportunity for price
correction.
The importance of SMT Divergence lies in its ability to detect hidden market dynamics that are
often manipulated by institutional players. By understanding these divergences, traders can
gain insights into potential market moves and position themselves accordingly.
2. The Relationship Between Correlated Markets
Understanding these relationships is crucial for identifying SMT Divergence:
Forex Pairs : Many Forex pairs have direct correlations. For example, EUR/USD and USD/JPY are often correlated in the sense that when the USD strengthens, both pairs may exhibit price movement in the same direction (EUR/USD decreases, USD/JPY increases). SMT
Divergence occurs when these pairs move in opposite directions, indicating that something
unusual is happening in the market (e.g., liquidity manipulation or market anticipation).
Indices : Stock market indices (like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones) and related instruments like futures or ETFs can show correlation. A divergence in these indices might indicate potential
trends or reversals, signaling that institutions are positioning themselves for a move in one
direction, and the market is showing resistance.
Bonds : The relationship between bond yields and currency pairs, for instance, can also show correlations. When bond yields move in one direction, certain currency pairs should
generally follow suit. Divergence in this relationship can reveal clues about market
intentions, such as shifts in interest rates or macroeconomic sentiment.
Commodities and Stocks : Commodities like oil and gold can often correlate with indices or specific stocks. For example, if oil prices rise and an energy sector index doesn’t move in the
same direction, this could be a sign of market inefficiencies or institutional positioning.
3. SMT Types
3.1. Bullish SMT Divergence
Bullish SMT (Smart Money Technique) Divergence occurs when one correlated asset forms a
higher low while another makes a lower low. This indicates that one market is showing hidden
strength, suggesting a potential reversal to the upside.
How to Spot Higher Lows in One Asset While the Other Makes Lower Lows:
1. Identify Two Correlated Markets – Choose two assets that typically move together, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD or NASDAQ and S&P 500.
2. Look for Divergence – Observe when one asset makes a new lower low, while the other fails to do so, instead of forming a higher low.
3. Volume & Price Action Confirmation – Institutions may absorb liquidity in the weaker asset while the stronger one holds its ground.
4. Validate with Market Context – Look at macroeconomic conditions, liquidity pools, and institutional activity to confirm the setup.
3.2. Bearish SMT Divergence
Bearish SMT Divergence occurs when one correlated asset forms a lower high while another
makes a higher high. This signals hidden weakness, indicating that the market may be setting
up for a bearish reversal.
How to Spot Lower Highs in One Asset While the Other Makes Higher Highs:
1. Find Two Correlated Markets – Common pairs include NASDAQ vs. S&P 500 or EUR/USD vs. GBP/USD.
2. Identify the Divergence – One asset makes a higher high, while the other fails to follow and forms a lower high instead.
3. Liquidity & Volume Analysis – Smart money may be using the stronger asset to attract buyers before reversing.
4. Confirm with Institutional Order Flow – Watch for liquidity grabs and imbalance zones.
3.3. Intermarket SMT
Definition : Divergence between assets from different markets, such as Forex vs. Commodities, Stocks vs. Bonds, or Indices vs. the U.S. Dollar.
Examples :
EUR/USD vs. DXY (U.S. Dollar Index) – If EUR/USD forms a higher low while DXY makes a
higher high, this suggests USD weakness and potential EUR/USD strength.
NASDAQ vs. S&P 500 – If NASDAQ makes a higher high but S&P 500 doesn’t, it can indicate
a weakening stock market rally.
Strength & Validity :
High validity because institutions hedge positions across different markets.
3.4. Intramarket SMT
Definition : Divergence within the same market (e.g., multiple Forex pairs or stock indices).
Examples :
EUR/USD vs. GBP/USD – If EUR/USD makes a lower low but GBP/USD doesn’t, it could
indicate bullish strength.
Dow Jones vs. S&P 500 vs. NASDAQ – If NASDAQ is making new highs while the Dow lags, it
may signal weakness in the broader stock market.
Strength & Validity :
Still valid but needs additional confirmation (liquidity sweeps, volume analysis).
4. SMT Divergence vs. RSI Divergence
Why SMT Is Superior to Traditional RSI Divergences
1. RSI Measures Momentum, Not Liquidity – RSI divergence is based on momentum shifts,
which institutions can easily manipulate with fake breakouts or engineered price moves.
2. SMT Focuses on Market Structure & Liquidity – SMT divergence detects institutional
positioning by comparing correlated assets, making it harder to manipulate.
3. RSI Can Remain Overbought/Oversold for Long Periods – Markets can continue trending
despite RSI divergence, while SMT divergence often provides stronger reversal signals.
How Smart Money Manipulates Classic Divergence Traders
Liquidity Sweeps – Institutions use RSI divergence to lure retail traders into premature
reversals before executing stop hunts.
False RSI Signals – In trending markets, RSI divergences often fail, while SMT divergence
provides a more contextual view of smart money positioning.
5. Using TradingView for SMT Analysis
To effectively analyze SMT divergence, traders should monitor at least two correlated assets
simultaneously.
TradingView makes this easy by allowing multiple chart layouts. Steps to Set Up Multiple Charts in TradingView:
a. Open TradingView and click on the “Select Layout” button.
b. Choose a two-chart or four-chart layout to compare correlated assets.
c. Sync timeframes across all charts for consistency.
d. Adjust scaling to ensure price action is easily comparable.
Best Pairs to Compare for SMT Analysis:
Forex : EUR/USD vs. GBP/USD, USD/JPY vs. DXY
Indices : NASDAQ vs. S&P 500, Dow Jones vs. S&P 500
Commodities & FX : Gold (XAU/USD) vs. USD/JPY
Bonds & Equities : 10-Year Treasury Yield vs. S&P 500
6. Key Takeaways
SMT divergence reveals institutional intent by showing liquidity accumulation or
distribution through correlated assets.
Bullish SMT occurs when one asset makes a lower low while the other does not, signaling a
potential reversal up.
Bearish SMT occurs when one asset makes a higher high while the other does not, signaling
a potential reversal down.
Best markets for SMT analysis include Forex pairs, indices, commodities, and bonds, where
correlations are strongest.
SMT is most effective near key liquidity levels, such as session highs/lows, order blocks, and
fair value gaps.
SMT is more reliable during high-impact news events, London & New York sessions, and
quarterly shifts, where institutional activity is highest.
SMT is superior to RSI divergence because it reflects real liquidity dynamics, whereas RSI
can produce false signals.
Combining SMT with market structure shifts like BOS and CHoCH increases trade accuracy
and reliability.
Risk management in SMT trading requires stop-loss placement beyond liquidity grabs and a
minimum 2:1 risk-reward ratio.
Mastering SMT helps traders avoid liquidity traps, improve precision, and align with smart
money moves.
SMT divergence is the footprint of smart money—where one market whispers the truth while the other follows the herd.
Wedge Pattern: A Key to Trend Reversals and Continuations📈 Wedge Pattern: A Key to Trend Reversals and Continuations
A wedge pattern is a technical chart formation that signals a potential reversal or continuation in the market. It’s formed when price moves between two converging trendlines — either sloping upward or downward — creating a narrowing range over time.
There are two main types of wedge patterns:
🔻 Falling Wedge (Bullish)
Formed during a downtrend or as a correction in an uptrend.
Characterized by lower highs and lower lows, with the slope of the support line steeper than the resistance line.
Typically signals a bullish reversal as momentum builds for a breakout to the upside.
✅ Confirmation: Break above the resistance line with volume surge.
🔺 Rising Wedge (Bearish)
Appears during an uptrend or as a correction in a downtrend.
Shows higher highs and higher lows, but the support line is steeper than the resistance line.
Often leads to a bearish reversal, especially when volume declines into the pattern.
⚠️ Confirmation: Break below the support line with increasing volume.
🧠 Key Characteristics
Volume tends to decrease as the pattern forms, indicating a pause in momentum.
The breakout direction (up or down) determines whether it’s a continuation or reversal signal.
Wedges can appear on any time frame and are useful for both day traders and long-term investors.
📊 Trading Tip
Always wait for confirmation of the breakout before entering a trade. False breakouts can be common, especially in low-volume environments
Smart Liquidity in TradingIntroduction: What Is Smart Liquidity in Trading?
Liquidity is the backbone of financial markets—it refers to how easily assets can be bought or sold without causing drastic price changes. But as markets have evolved with the rise of algorithmic trading, decentralized finance (DeFi), and AI, a more sophisticated concept has emerged: Smart Liquidity.
Smart Liquidity isn’t just about having buyers and sellers in a market. It’s about efficient, dynamic, and intelligent liquidity—where technology, data, and algorithms converge to improve how trades are executed, how markets function, and how risks are managed. Whether in traditional stock markets, forex, or blockchain-based platforms, smart liquidity is now central to modern trading strategies.
Chapter 1: Understanding Traditional Liquidity
Before diving into smart liquidity, let's revisit the basics of traditional liquidity:
Bid-Ask Spread: A narrow spread indicates high liquidity; a wide one shows low liquidity.
Market Depth: The volume of orders at different price levels.
Turnover Volume: How frequently assets are traded.
Price Impact: How much a large order moves the price.
In traditional finance, liquidity providers (LPs) include:
Market makers
Banks and financial institutions
High-frequency trading firms
Exchanges
Liquidity ensures:
Stable pricing
Smooth trade execution
Lower transaction costs
Chapter 2: The Evolution Toward Smart Liquidity
What Changed?
Algorithmic Trading: Algorithms can detect, provide, or withdraw liquidity in milliseconds.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Smart contracts offer on-chain liquidity pools without intermediaries.
AI & Machine Learning: Predictive models can identify where liquidity is needed or likely to shift.
Smart Order Routing (SOR): Optimizes trade execution by splitting orders across multiple venues.
These technologies gave rise to “smart liquidity,” where liquidity is not static but adaptive, context-aware, and real-time optimized.
Chapter 3: Components of Smart Liquidity
1. Liquidity Intelligence
Advanced analytics track:
Market depth across exchanges
Order flow trends
Latency and slippage statistics
Arbitrage opportunities
This helps institutions dynamically manage their liquidity strategies.
2. Smart Order Routing (SOR)
SOR systems:
Automatically split large orders across venues
Route based on fees, liquidity, latency, and execution quality
Reduce market impact and slippage
SOR is key in both equity and crypto markets.
3. Algorithmic Liquidity Providers
Market-making bots adjust quotes in real-time based on:
Volatility
News sentiment
Volume spikes
Risk exposure
They enhance liquidity without manual intervention.
4. Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Used in DeFi:
No traditional order book
Prices determined algorithmically via a liquidity pool
Traders interact with pools, not people
Popular AMMs: Uniswap, Curve, Balancer.
Chapter 4: Use Cases of Smart Liquidity
1. HFT Firms and Institutions
Use predictive liquidity models
Deploy SOR to reduce costs and slippage
Balance exposure across markets
2. Retail Traders
Benefit from tighter spreads and faster execution
Use platforms with AI-driven order matching
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Anyone can provide liquidity and earn fees
Smart liquidity enables 24/7 trading with no intermediaries
New protocols optimize capital allocation via auto-rebalancing
4. Stablecoin & Forex Markets
Smart liquidity ensures 1:1 peg stability
Algorithms prevent arbitrage imbalances
Chapter 5: Key Metrics to Measure Smart Liquidity
Metric Description
Slippage Difference between expected and actual execution price
Spread Efficiency How close bid-ask spreads are to theoretical minimum
Fill Rate How much of an order is filled without delay or rerouting
Market Impact Price movement caused by a trade
Liquidity Utilization How efficiently capital is allocated across pairs/assets
Latency Time taken from order input to execution
These metrics help evaluate the quality of liquidity provided.
Chapter 6: Risks and Challenges of Smart Liquidity
Despite its benefits, smart liquidity isn’t perfect.
1. Flash Crashes
Caused by sudden withdrawal of liquidity bots
Example: 2010 Flash Crash in U.S. equities
2. Manipulation Risks
Predatory algorithms can spoof or bait other traders
"Liquidity mirages" trick algorithms
3. Smart Contract Failures (DeFi)
Vulnerabilities in AMMs can drain entire liquidity pools
Hacks like those on Curve and Poly Network show smart liquidity can be fragile
4. Impermanent Loss (DeFi)
LPs may lose value if asset prices diverge significantly
Complex math and simulations needed to manage it
5. Regulatory Uncertainty
Especially in crypto, regulators still debating on decentralized liquidity protocols
Conclusion
Smart liquidity represents the next evolution of market infrastructure. It's not just about having capital in the market—it's about how that capital moves, adapts, and executes.
From hedge funds deploying intelligent routing systems to DeFi users earning yields through AMMs, smart liquidity touches every corner of modern finance. As technology continues to mature, expect liquidity to become even more predictive, responsive, and intelligent—unlocking a new level of speed, precision, and access for traders around the world.